Perpetually Adaptive Enterprise
At TCS, we don’t just help businesses transform. We help them become perpetually adaptive enterprises, built to evolve continuously and confidently in a world of constant change.
- Banking
- Capital Markets
- Consumer Packaged Goods and Distribution
- Communications, Media, and Information Services
- Education
- Energy, Resources, and Utilities
- Healthcare
- High Tech
- Insurance
- Life Sciences
- Manufacturing
- Public Services
- Retail
- Travel and Logistics
- Artificial Intelligence and Data & Analytics
- Cloud
- Cognitive Business Operations
- Consulting
- Cybersecurity
- Enterprise Solutions
- Industrial Autonomy & Engineering
- Network Solutions and Services
- Sustainability Services
- TCS Interactive
About Us
We deliver excellence and create value for customers and communities - everyday. With the best talent and the latest technology we help customers turn complexity into opportunities and create meaningful change.
TCS Insights
Point of views, research, studies - on the latest themes - to help you expand your knowledge and be future ready.
Recent recognitions
View allWant to be a global change-maker? Join our team.
At TCS, we believe exceptional work begins with hiring, celebrating and nurturing the best people — from all walks of life.
Top Results
In the 21st century, customer data is one of the most coveted possessions. The successful commoditization of end-user’s data had led to the exponential growth of the five best performing American technology companies (FAANG+). This initiated the rat race of data collection and fueled the need for data privacy and protection. Stringent data regulations were formulated like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). They brought a tectonic shift in data protection, from being ‘good-to-have’ guidelines to ‘must-have’ mandates. However, these guidelines posed a sudden challenge towards adherence. After thorough contemplation, data anonymization was identified as one of the most trusted and recognized industry solutions. It is a process of identifying personal details and replacing them with fictitious, but realistic values that preserve data utility. The next big hurdle was the implementation of anonymization across the enterprise.
Implementing Data Anonymization – Challenges
The key challenges can be categorized as follows:
- Data classification:
- What are personal and business sensitive details?
- Which applications store sensitive information?
- Privacy definition:
- How to identify sensitive details?
- How to mask sensitive data?
- Stakeholder coordination:
- How to build consensus for data anonymization?
- How to assess the impact of change?
- Enterprise level anonymization solution:
- How to identify products supporting wide range of data sources?
- Skill set for implementation
- How to handle the lack of in-house implementation experience?
Five Phased Methodology for Data Anonymization
Being a niche and new area, data anonymization should follow a phased approach for enterprise-wide implementation. TCS suggests a ‘Five Phased Methodology’ depicted as follows:
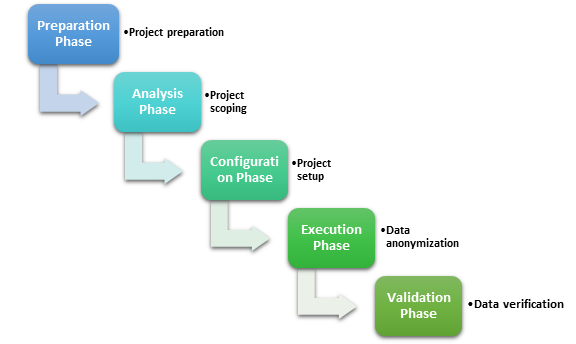
Figure 1: Five Phased Methodology for Data Anonymization
Preparation Phase
The owner of the data privacy program initiates the project. The scope is derived by assessing applications in the IT landscape. Data privacy regulatory compliance is the key driver for the requirements list.
The key activities are:
- Creating the project charter to establish the objectives and success criteria.
- Bringing the stakeholders on-board towards a consensus on the implementation approach.
- Identifying the applications and data sources to be included in the project scope.
- Finalizing the data privacy definition for the enterprise.
- Procuring the required infrastructure for the implementation, including data anonymization products.
Analysis Phase
The implementation team follows the data privacy definition and work scope to perform the due diligence.
The key activities are:
- Analyzing the data sources for inter-dependency and presence of personal data.
- Performing due diligence to understand the complexity of the application and data environment.
- Gathering data anonymization requirements for the identified sensitive attributes.
- Creating data privacy strategy to map sensitive attributes with required anonymization rules.
- Discovering sensitive data. (Tip: Use a data anonymization product with built-in sensitive data discovery feature).
- Defining test cases to validate the quality of masked data.
- Ensuring review and approval of the data anonymization policy by the data compliance team.
Configuration Phase
Data privacy implementation is a unique exercise for each enterprise. After data anonymization strategy is verified, rules are configured using the selected anonymization product.
(Tip: A good data anonymization product should provide an automated and easy-to-use graphical interface for configuring the anonymization rules using built-in templates.)
The key activities are:
- Configuring the data anonymization product according to the data privacy requirements.
- Defining data constraints and relationship over sensitive attributes.
- Creating customized data sets to be used as masked values.
- Creating jobs to apply data anonymization rules to sensitive attributes.
Execution Phase
After data anonymization configuration is ready and verified, it is time for execution.
The key activities are:
- Executing the data anonymization process to refresh masked data in target environment.
- Generating reports to capture statistics and summary of the data anonymization process.
Validation Phase
Data validation is a mandatory step for checking sanctity of the masked target data environment – both for integrity of business rules and protection of personal details.
The key activities are:
- Running business test cases in masked environment.
- Checking for possibilities of reverse engineering of personal identity.
- Sharing review comments on the anonymization process for bridging any gaps.
Data Privacy Governance
A system is bound to fall apart in the absence of good governance, despite a strong design. An established governance system ensures continuity of usual operations and continuous enhancements to keep the system relevant. Data privacy governance constitutes of the following components:
- People – the stakeholders
- Process – the rules and workflows
- Technology – the enablers

Figure 2: Data Provisioning Process
A centralized test data management team is preferred for implementing the data provisioning process, while the governing body ensures discipline through the set processes and usage of the tools.
About the author
Rahul Ghodeswar
Related reading
Sovereign Cloud: Guardians of the Digital Frontier
Modernise ETL Systems for a Successful AI-first Operating Model
Lifting the Partial Observability Cloud to Enable HyperOps
Remote Work and its Role in Reshaping Mortgage Lending Practices