Industry
Highlights
- In an era defined by relentless change, organizations that are perceptive will have the ultimate competitive advantage.
- Perceptive RetailTM is a paradigm shift in how retailers do business.
- It harnesses the interplay of three factors: reasoning-based decision intelligence, nuanced insights from multimodal data, and the autonomy of machine agents to generate intelligent choices for smarter decisions and better business outcomes.
On this page
What is perceptive retailTM?
The emergence of agentic artificial intelligence (AI), generative AI (GenAI), and advancements in real-time processing power are helping retailers infer meaning from complex data and be more perceptive.
In an era defined by relentless macroeconomic shifts, evolving customer expectations, and intense competition, the ability to decode market signals, spot opportunities before they manifest, and act decisively is the ultimate competitive advantage. This requires a new level of organizational perceptiveness: the ability to understand the deeper context from data.
Today’s retailers have access to unprecedented pools of data on customers, inventory (distribution center and store), operations, financials, and competition. Much of that data is multimodal and unstructured. Until now, most retailers have struggled to infer meaning from this complex data. That is changing with the emergence of novel technologies such as agentic AI, GenAI, and advancements in real-time processing power. Together, they dramatically increase the ability of enterprises to be perceptive. As per the TCS Global Retail Outlook study, right now about 24% retailers are using AI for autonomous decisions while 85% have not planned or started implementing multi-agent systems, imperative for an effective AI enterprise strategy.
The ability to decode market signals, spot opportunities before they manifest, and act decisively, is the ultimate competitive advantage.
Perceptive RetailTM is a paradigm shift in how retailers do business. It harnesses the interplay of three factors: reasoning-based decision intelligence, nuanced insights from multimodal data, and the autonomy of machine agents to generate intelligent choices for smarter decisions and better business outcomes. It is driving innovation in workforce models, retail operations, and customer experience.
Shifting human-machine dynamics
Over the years, we’ve seen a paradigm shift from a world where technology supports human efforts to one where technology is an integral actor within the workforce.
Take the process of gleaning competitor intelligence. Historically, data for sensing the market and monitoring competitors was collected manually via store visits, websites, and industry reports. Item matching was manual and data was input into computers. Its timeliness was suspect and its scale limited. Dashboards presented static visualizations, and decision-making was reactive. With the arrival of AI, data capture and item-matching were automated, but decisions still relied on dashboards.
Now, AI agents mine competitor data at a scale and speed previously unimaginable. They can analyze prices as well as promotions, assortment, and content at a zip-code level. Multimodal capabilities allow them to generate qualitative commentary on the strategic intent of competitors in natural language. With a big picture view, decision-making is elevated from a tactical to strategic level.
By responding to competitor moves in real time, retailers gain tangible benefits. These include double-digit growth in revenue and sales of key categories, customer retention, and productivity.
This study reveals that retailers prioritizing AI-driven dynamic pricing, demand forecasting and inventory optimization, and supply chain optimization are positioning themselves for sustainable competitive advantage.
Moving from better processes to better choices
Perceptive Retail involves reimagining every aspect of business.
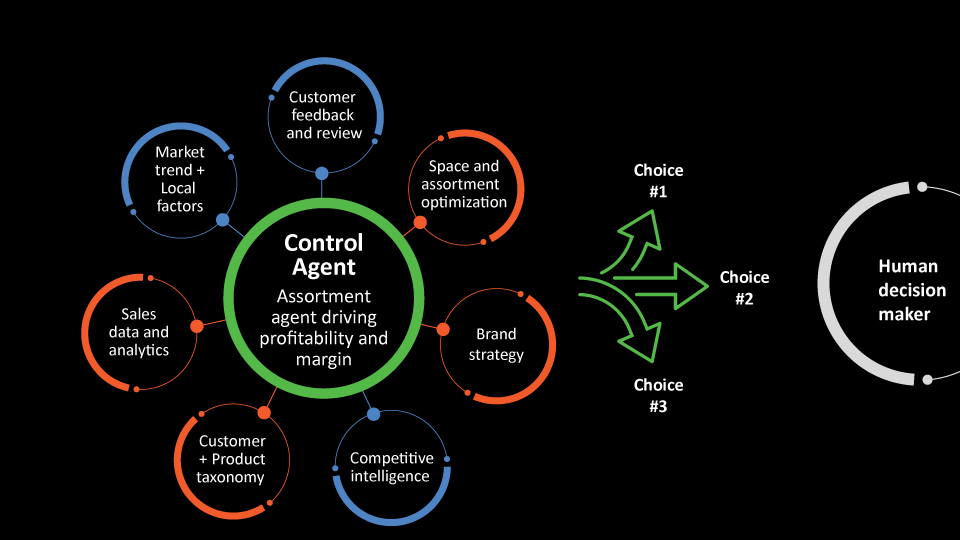
Consider the classic retail task of introducing a new item to an assortment. Traditionally, this decision has been time-consuming and has rested with a small cohort of senior personnel. Perceptive Retail changes this formula. Multi-agent systems (Figure 1) augment the capabilities of category managers, enabling them to nimbly adapt assortments, balancing consumer trends, market demand, and profitability.
Goal-oriented agents powered by generative and predictive AI play designated roles. The customer feedback agent monitors customer interactions, transaction history, social media, trending news, and a wide range of unstructured data sources. The competitor intelligence agent scans competitor assortments from websites and flyers. It spots that a key competitor has introduced a new item, such as licorice and chili-flavored tuna fish. Another agent tracks market trends—infers an uptick in demand for Asian flavors—and checks the opportunity by referencing market research reports in whatever format they exist.
The control agent then orchestrates a response. It coordinates with the other agents that identify brand incongruities, forecast demand, and propose stores receptive to new items. The space and assortment agent uses simulations and optimization tools to craft tailored assortment options.
Perceptive Retail helps businesses thrive in a dynamic market with foresight, agility, and precision by providing intelligent choices for smarter decisions.
The control agent evaluates options proposed against the business key performance indicators (KPIs) and presents well-reasoned, intelligent choices, supported by chain-of-thought reasoning and quantitative insights. The category manager may choose to change the assortment, for example, in stores where Asian flavors are preferred. In doing so, the manager grabs the opportunity to drive profit, margins, and customer experience (CX). Other tangible benefits include hyper-localized assortments and higher inventory availability. This can be immensely valuable for big grocery and fast fashion retailers.
The control agent learns from human decisions and business outcomes and refines the underlying AI models, codifying the tacit knowledge of experts into institutional wisdom. In future, the agent will offer even more refined choices. Category managers with varied experience and skills can make faster, better, and more decisions.
Due to their non-linear nature, machine agents can be integrated across business functions to fulfill a range of tasks such as optimized price points, in-store facings, and supply chain distribution. Their capabilities can also extend beyond the enterprise, connecting vendors, partners, and customers into a boundaryless retail ecosystem.
Inferring unstated needs and deeper context
In the past, retail personalization relied heavily on structured data, such as clicks, views, and purchase history.
These systems operated on static models, providing insights based on intent or past behavior. They struggled to understand the broader context or infer deeper customer needs. By leveraging smart sensing, Perceptive Retail transforms personalization into a proactive, context-aware, customer-centric process.
Meet Lisa, newly married with a first home to furnish. She needs sound advice when it comes to the big purchases of home appliances such as a refrigerator. As a freelancer with a variable income, Lisa needs more than just product recommendations. She needs a shopping companion that understands her aspirations and constraints. She uses the intelligent buying guide on an ecommerce site, engaging through voice.
The digital agent powering the buying guide picks up signals from natural language inputs and discerns Lisa’s excitement. It understands her context, such as financial restraints, and infers unstated needs, for example, budget options. It can suggest if, by buying multiple appliances from a single brand, there is a deal to be had or if there are smart financing options available. Factoring in the size of the kitchen from a photo and considering the family’s consumption patterns, the agent recommends suitably sized choices. Lisa is presented with choices she might not have considered otherwise. Additionally, the agents adapt their recommendations in real-time and combine precise product suggestions with tailored promotions, engaging content, and flexible delivery options.
The intelligent buying guide provides ‘white glove’ customer service to each customer. For retailers, it produces a double-digit uplift in conversions, higher average order values, customer lifetime values, and net promoter scores. Store associate and contact center agent training times are reduced.
Transforming into a perceptive retailer
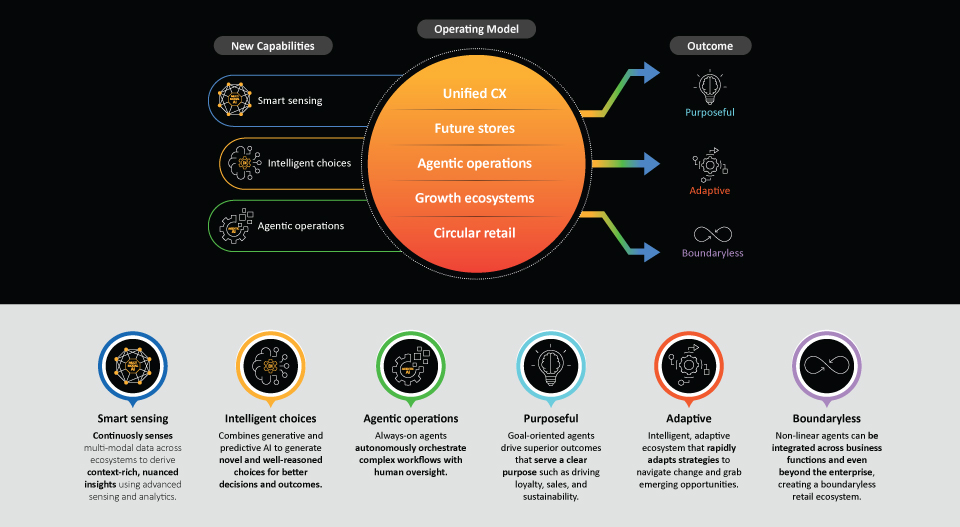
Perceptive Retail integrates smart sensing, intelligent choices, and agentic operations to build purposeful, adaptive, and boundaryless enterprises.
In a fast-changing economic and competitive landscape, these retailers win with foresight, agility, and precision. Gaining a competitive edge requires a strong focus on five key pillars: unified CX, future stores (five key pillars: unified CX, future stores, agentic operations, growth ecosystems, and circular retail (Figure 2).
Our study reveals that retailers are prioritizing a blend of advanced analytics, risk management, and organizational adaptability to stay ahead of disruption. The leading approaches—from leveraging AI for predictive forecasting to strengthening supplier relationships—are shaping the industry’s new playbook for operational agility.
It is important to recognize that this transformation into a perceptive retailer is not just about technology. Delivering intelligent choices that drive smarter decisions is key to realizing business outcomes. Success factors include knowing where and how to introduce machine agents; encoding decision-making built on both tacit and explicit knowledge; and establishing clear KPIs in collaboration with business leaders. Building AI trust requires implementing guardrails, continuous testing, and coaching to ensure accuracy and reliability of output. Finally, Perceptive Retail entails enterprise-wide change management. Business functions will need to be reconfigured if the business is to experience seamless collaboration between humans and machine agents.