Industry
Highlights
- Warehouse operators need to understand how utilizing the metaverse can improve their operations.
- Metaverse also has the capability to synchronize with digital twins to virtualize the operations and optimize the workflows of the warehouse.
- Warehouse employee efficiency and safety can be improved by virtual training and guided work instructions.
On this page
Summary
Warehouses play a pivotal role in supply chain operations, not only as storage centres, but also as transportation hubs, just-in-time (JIT) fulfilment centres and risk mitigation points.
We are seeing the Metaverse emerge as an option to help warehouse operations with minimal disruption to the business. Visually simulating warehouse layouts and activities unlock new dimensions of planning, optimization, and decision-making. This can help businesses to improve operational efficiencies and throughput while also enabling key tasks like warehouse optimization, future scenario planning and new employee training.
Warehouse optimization moving from CAD drawings to Virtual Reality (VR) allows the operations team to visualize the changes before they move even a single piece of racking. When combined with Warehouse Twins—a digital replica of physical warehouse operations—the metaverse offers a highly immersive and interactive approach to optimize the warehouse performance.
These visualizations are also powerful to assess how future changes in volumes and workflows will impact warehouse operations. Accurately forecasting future impacts has increasingly become challenging for operations teams. The impacts include the potential use cases for automation within the warehouse. The lack of visualization to truly support this type of scenario planning is an important need that has not been addressed in detail and VR may play a role in its viability.
The Metaverse also has a key role in improving efficiency in day-to-day activities. It is quite common to have new employees or temporary workers that need to be trained for jobs in the warehouse. A VR program will provide a means to enable efficient and effective training for these new employees that requires less involvement from existing resources while providing visual task training.
Warehouse Operations
There has been a transformation in warehouse operations due to the advancements in technology.
Warehouse operations have transitioned from manual processes to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) systems, thus digitizing transactions, providing comprehensive analytics and dashboards, and optimizing processes with an end-to-end view. Automation systems are enhancing warehouse operations by reducing manual interventions and increasing efficiency. The metaverse is gaining popularity for its ability to augment real-world features and transpose reality into virtual environments.
Adoption of technology remains slow in the warehouse space because of factors such as costs, resource availability, maintenance, hindrance to change management etc.
Warehouse’s face several operational challenges, a few of them being:
- Acclimatizing to changes in workflows
- Low fulfilment rates
- Safety of personnel and material handling equipment
- Real time visibility
- Very less space to experiment the changes and visualize the results.
- Training and development
Modifying warehouse workflows can be quite challenging during normal operations. Most warehouses have high uptime and limited downtime during off hours when staffing is not available. So, when a warehouse changes its workflows, one needs to account for potential disruptions. Most organisations mitigate these disruptions by customizing one area at a time. For example, customizing the picking area before moving to the shipping area in a logistical organisation would be better. These changes can be difficult to rationalize because most operations do not have sufficient tracking devices and rely on eye tests.
Employee training typically accompanies planned changes to the warehouse layout. Long-term personnel may find it challenging to adapt, so on-the-job training is often conducted during workflow evaluations. Training in batches ensures everyone stays aligned. However, new employees and temporary workers are an exception that must be trained on an ‘as required basis.’ This can be challenging as the warehouse is often shorthanded when these new additions come on board. These employees usually start with the simplest tasks and rely on standardized work instructions to complete their assigned tasks for the day.
Role of Metaverse
Metaverse is a pseudo reality environment which augments or completely mimics the real environment in a virtual world. This can be achieved in various ways – augmented, virtual or mixed realities.
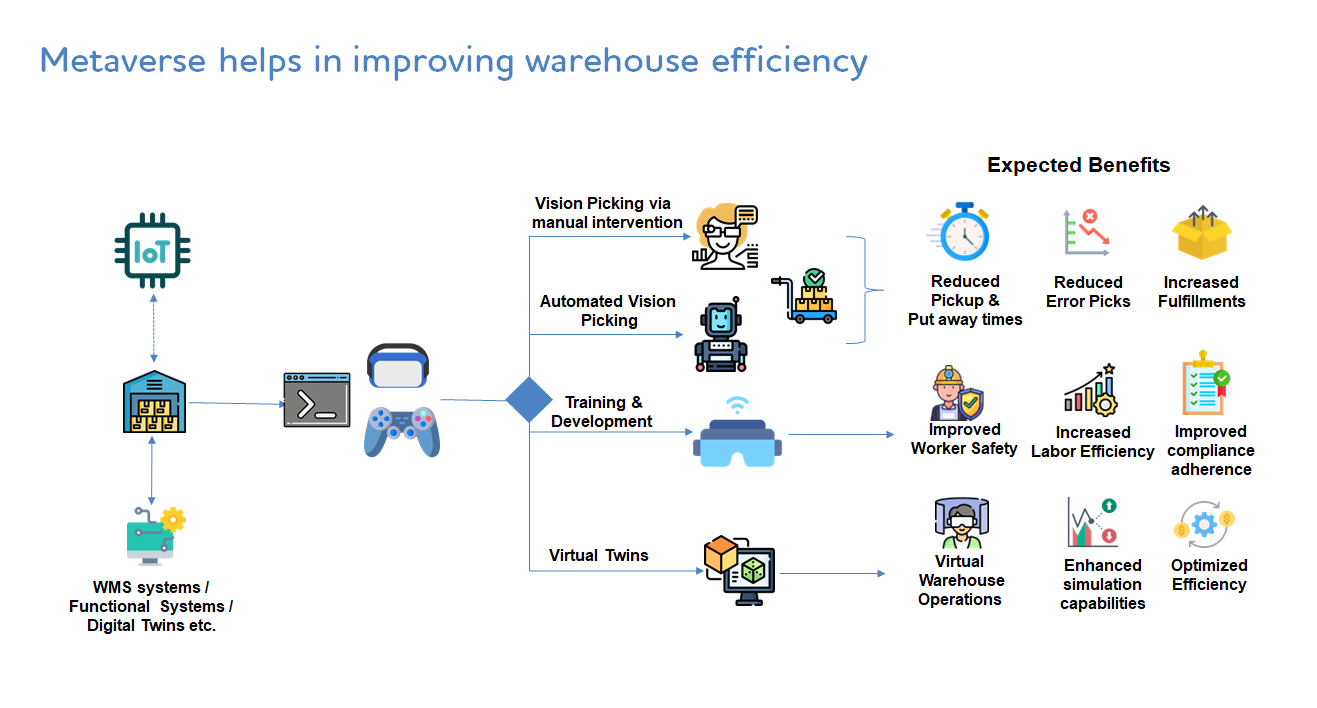
The rising adoption of the metaverse is reshaping traditional perspectives on warehouse operations. By harnessing its advanced visualization and simulation capabilities, organizations can model workflows, conduct training, and perform analysis without interrupting ongoing activities.
The metaverse serves as an extension of the Warehouse Management System (WMS), leveraging active Internet of Things (IoT) devices within the warehouse to visually represent real-time operations. These activities can be modified to provide ‘what-if scenarios’ that can facilitate continuous improvement.
Revamped warehouse designs can significantly enhance operational efficiency, allowing companies to validate improvements virtually before committing to physical assessments or pilot implementations.
Functional Tenets
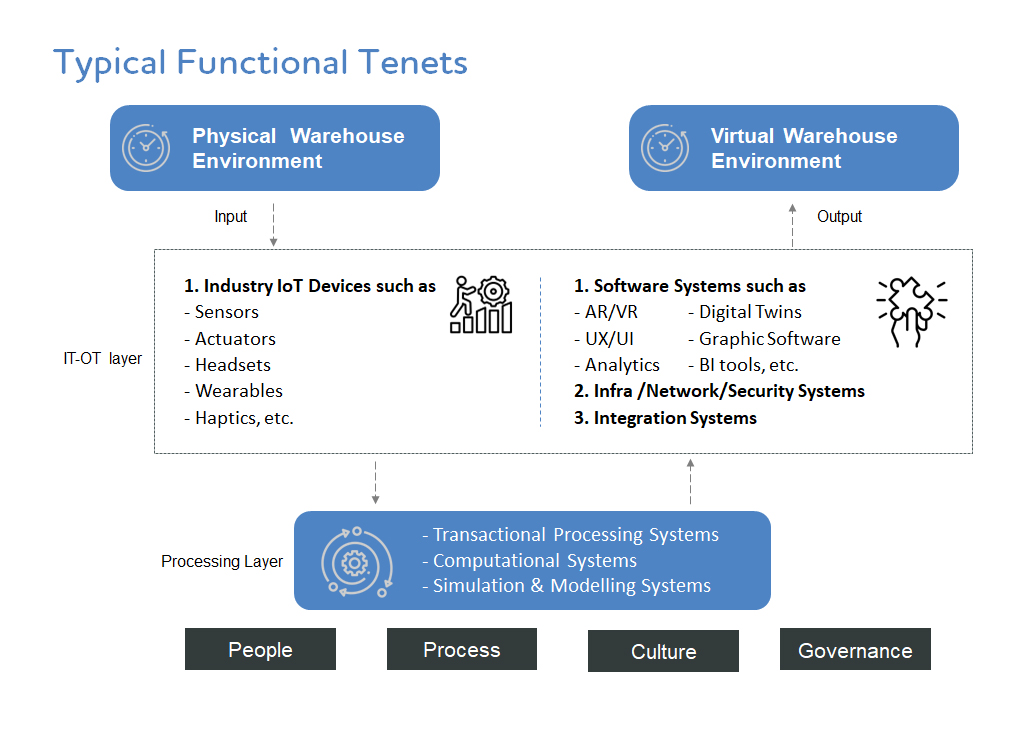
The functional architecture of a metaverse application for warehouse operations can range from simple to highly complex, depending on specific business needs and operational goals.
This is achieved by simulating the real-time warehouse environment within a virtual world and integrating it with IT-OT systems, warehouse applications, and other digital infrastructure. The image below illustrates the key functional tenets required to build such a virtual environment.
Sustainable Operations
Metaverse applications are rapidly transforming warehouse operations, introducing new levels of efficiency, agility, and insight. We explore key use cases and how these innovations are driving smarter, more connected warehouse environments.
Picking and putaway operations consume significant time in order fulfillment. In dynamic warehouse environments, tracking SKU storage locations has always been a challenge. Augmented Reality (AR) guided headsets assist in the vision picking process by directing pickers to the correct rack locations, thus eliminating the need for manual scanning. This enhances warehouse efficiency by reducing pick and putaway times, minimizing errors, and improving fulfillment efficiency. AR headsets support both audio and video instructions, surpassing other methods like pick-by-voice or pick-by-light.
Warehouse environments present a range of safety challenges due to the presence of diverse material handling systems such as forklifts, conveyors, and manual operations; specialized storage requirements for items like hazardous materials, chemicals, food products; and high volumes of loading and unloading activities across multiple locations including docks and yards. As a result, ensuring safety has always been a critical priority in warehouse operations.
Configurating virtual warehouse environment and training the warehouse personnel not only helps personnel in experiencing best practices but also in experiencing the dangers associated with malpractices.
Metaverse has revolutionized warehouse design. Personnel can experience virtual twins and experiment with multiple scenarios, allowing them to predict efficiencies in a virtual environment and implement effective scenarios in real time.
Metaverse Applications
Despite significant benefits, there are also challenges associated with implementing metaverse for industrial applications.
So, what is stopping the widespread adoption of utilizing the Metaverse in Augmenting Warehouse Operation?
- Awareness: Utilizing the metaverse is not yet a common approach for continuous improvement. Many warehouse managers are still very tactical and are not familiar with where the technology stands today and what are its applicable use cases.
- Cost: Adopting this technology demands a substantial investment, making it most viable for large-scale and complex warehouse operations where the potential for meaningful Return on Investment (ROI) justifies the commitment.
- Security: It is necessary to ensure that the appropriate safeguards are in place when you start moving data out of an established environment and into a Digital Twin and/or offsite data model.
- Identity Management: This poses a significant challenge as multiple real-world personas are converted into unique virtual avatars or assets, requiring tokenization. Privacy concerns also arise with the evolving use of public and private blockchain platforms.
- Partners: Embracing the metaverse for warehouse operations requires selecting the right technology partner—one capable of guiding implementation and integration. Given the complexity involved, this often exceeds the capabilities of in-house teams, making external expertise essential for success.
Final Thoughts
Metaverse holds immense potential—from shaping the design and development of new warehouses to enhancing operational efficiency in existing facilities.
Since safety is of paramount importance, metaverse can play a huge role in improving safety by training and development of warehouse personnel and by using for virtual or semi virtual operations.
The potential of the metaverse in warehouse operations opens transformative possibilities that once seemed out of reach. Traditionally, gaining insights into warehouse activities has required physical site visits. However, in the near future, virtual Gemba Walks could become a reality—enabling continuous improvement initiatives to be conducted remotely, without ever stepping into a physical warehouse.
Though there are challenges associated, considering the evolving nature of the application, implementation teams should thoroughly study the ways to mitigate the risks. Businesses should analyse the trade-offs and use this technology based on their specific needs and benefits they aim to achieve.