Industry
HIGHLIGHTS
- Omnichannel retail, spanning websites, mobile applications, social media, IoT-enabled in-store kiosks, and voice assistants, has witnessed constant evolution, especially over the past few years, backed by complex systems.
- These complex omnichannel systems require rapid and continuous validation, given the frequent product releases, high user expectations, peak load periods during sales and holidays, and the need for compliance and security.
- Agentic AI-based test automation offers intelligence and adaptability to omnichannel retail systems by autonomously identifying, executing, and improving test scenarios across web, mobile, and in-store platforms.
On this page
Constant evolution
The retail industry is consistently undergoing transformations and digital advancements as witnessed in the rapidly evolving e-commerce platforms, dynamic pricing engines, enhanced omnichannel experiences, and accelerated release cycles.
Specifically, omnichannel retail has been a key area of constant evolution powered by systems that are inherently complex, spanning websites, mobile applications, social media, internet of things (IoT)-enabled in-store kiosks, voice assistants, and more. About 34% of pacesetters among the retailers polled for the TCS Global Retail Outlook Survey are prioritizing the creation of unified commerce platforms to ensure seamless shopping across all channels.
The integration of multiple point-of-sale (POS) systems, inventory and supply chain management platforms, customer loyalty programmes, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, payment gateways, and third-party application programming interfaces (APIs) further increases this complexity.
An adaptive agentic artificial intelligence (AI) model for test automation, specifically tailored to the unique demands of the omnichannel retail sector, can help solve the challenges.
Per the TCS Global Retail Outlook Survey, despite the overall enthusiasm around AI, the full potential of the technology remains largely untapped. Although, most retailers are leveraging AI for chatbots, virtual assistants, and AI-generated content only a few have advanced to more strategic uses. For example, about 24% respondents polled by the study are using AI-powered technology to make autonomous decisions, while 85% have not planned or even started implementing multi-agent systems to achieve their business goals.
Employing agentic AI
Complex omnichannel systems require rapid and continuous validation given the frequency of product releases, high user expectations, peak load periods (such as sales and holidays), and the need for compliance and security.
However, traditional test automation approaches, which rely on static scripts and fragile test data dependencies, are increasingly falling short of the requirements. There’s a pressing need for a different approach for test automation within the retail omnichannel landscape. In addition, to ensure quality at scale without sacrificing speed, retail businesses must adopt a fundamentally new approach to software testing.
The agentic model of test automation framework represents an emerging paradigm inspired by AI agents and autonomous systems. Unlike traditional automation frameworks, it incorporates intelligence, decision-making, and autonomy directly into the testing process. The result is a next-generation framework aligned with the critical business objectives of modern retail platforms, such as seamless checkout experiences, inventory accuracy, recommendation engine stability, and pricing integrity.
Employing an agentic AI model for test automation offers transformative potential by enabling intelligent, autonomous, and adaptive testing processes.
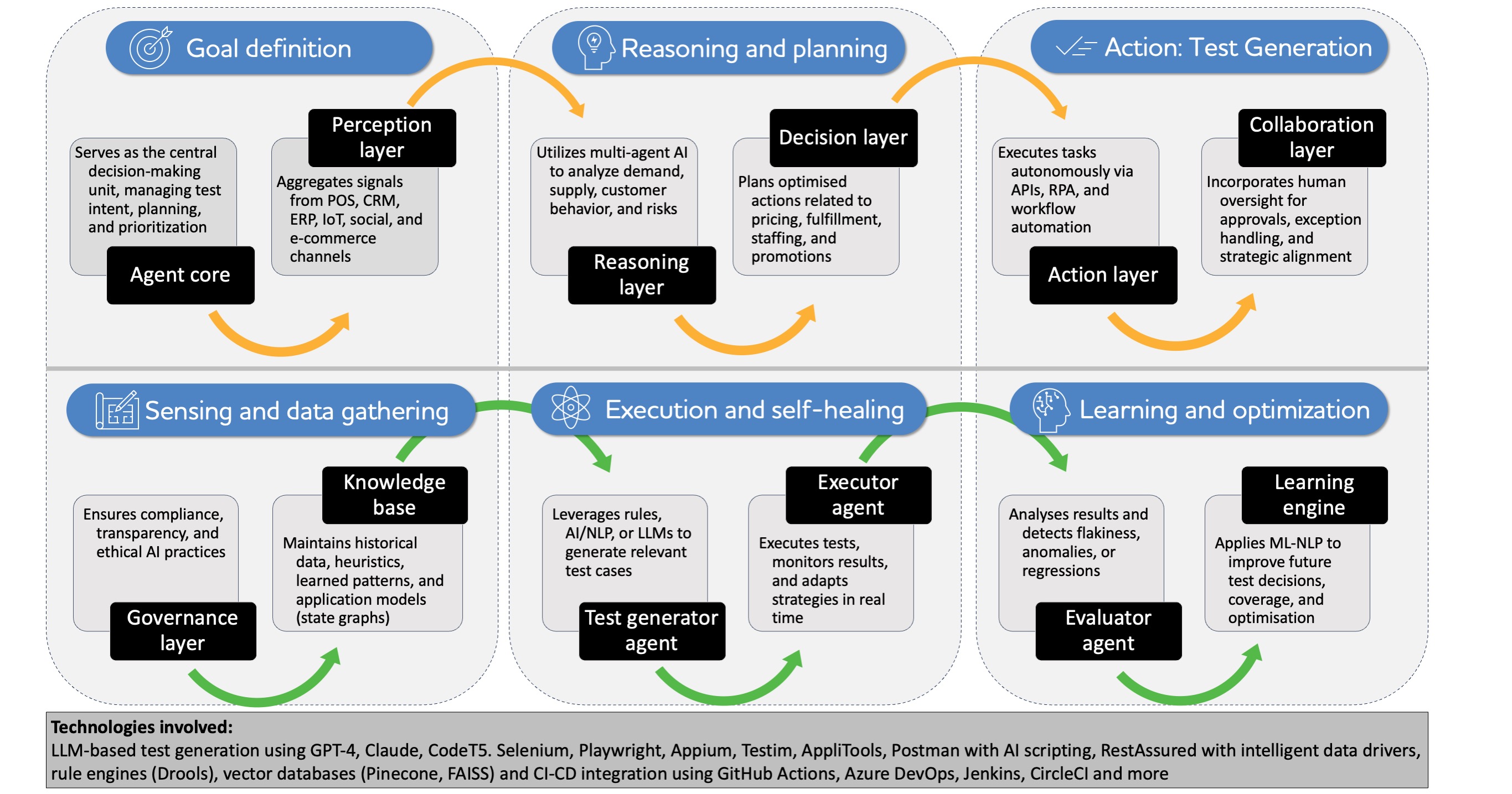
The framework
An agentic test automation framework is created around autonomous software agents capable of:
- Sensing their environment, including the application under test, logs, and data sources
- Reasoning and making decisions based on defined goals, rules, or AI models
- Acting by generating, executing, and adapting test cases dynamically
- Learning from execution outcomes to continuously enhance performance
This approach draws on principles from agent-based systems, generative AI (GenAI), and reinforcement learning, and typically aligns with GenAI-based testing strategies (see Figure 1).
Challenges and solutions
Omnichannel retail, which integrates online, offline, and mobile shopping experiences, faces several challenges.
Retailers struggle to synchronise data across systems, manage real-time inventory visibility, and ensure consistent pricing and customer experience across channels.
In addition, logistics have become complex with multi-source fulfillment, returns, and last-mile delivery costs. High technology investment, staff training, and maintaining a unified customer service add to the challenges because of organisational silos and data privacy compliance requirements, further complicating operations. Overall, while omnichannel retail offers convenience and reach, it demands strong coordination between technology, logistics, and people to deliver a seamless and profitable experience. Agentic AI is a powerful tool to help achieve these goals.
| Sl.No | Functional area | Challenge | Agentic AI mitigation |
| 1 | Fragmented customer data | Customer profiles are distributed across e-commerce, stores, apps, and loyalty platforms, resulting in an incomplete view of shopper behaviour. | Customer identity agents unify profiles across channels; journey mapping agents track real-time interactions; recommendation agents personalise offers dynamically. |
| 2 | Inventory visibility and synchronization | Stock discrepancies across channels and inefficient fulfillment decisions. | Inventory agents reconcile POS, warehouse management system (WMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and supplier data; fulfillment orchestration agents optimise order routing; predictive agents forecast demand and adjust allocations. |
| 3 | High fulfillment and logistics costs | Last-mile delivery and returns are costly; manual decision-making leads to suboptimal routing. | Logistics optimisation agents select optimal carriers, routes; returns automation agents streamline approvals and restocking; carbon-efficient route agents promote sustainability. |
| 4 | Personalisation at scale | Customers expect real-time personalisation; traditional rule-based methods do not scale with dynamic demand. | Engagement agents deliver hyper-personalised content; content curation agents adapt storefronts or app user interfaces (UIs); voice, chat AI agents provide individualised recommendations. |
| 5 | Channel silos and poor orchestration | Lack of synchronisation between channels disrupts seamless experiences. | Campaign orchestration agents align promotions across all channels; order lifecycle agents manage end-to-end flows; collaboration agents escalate exceptions to humans as needed. |
| 6 | Fraud and security risks | Omnichannel setups increase vulnerability to fraud and security breaches. | Fraud detection agents monitor transactions; behavioural AI agents identify unusual patterns; compliance agents automate regulatory reporting. |
| 7 | Workforce and store operations | Store associates face challenges supporting omnichannel functions; labour costs rise with inefficient scheduling. | Workforce scheduling agents optimise staffing; in-store task agents guide associates; training agents deliver contextual micro-learning. |
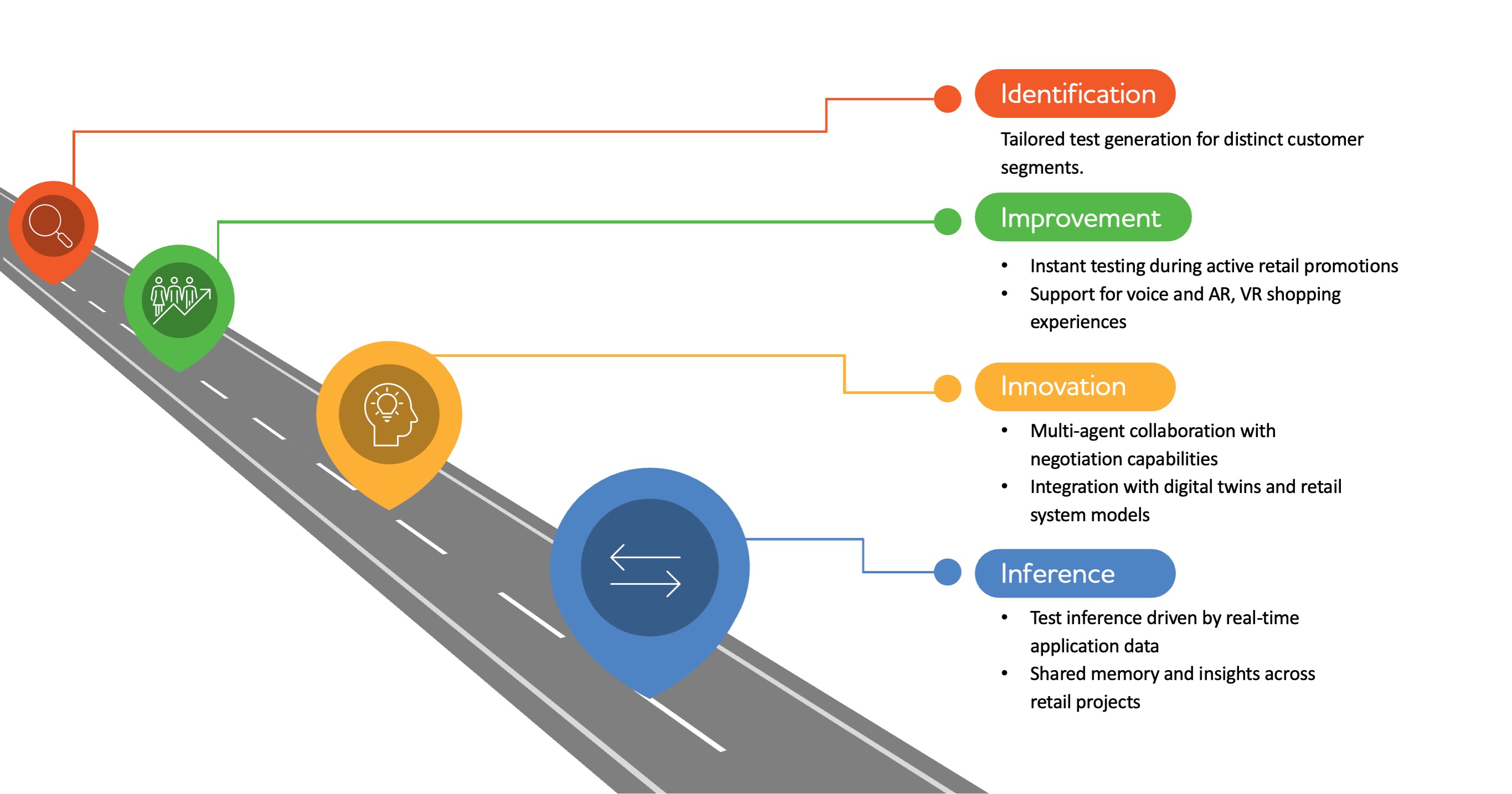
Implementation road map
Retailers need to begin with a flexible, modular testing framework that is easy to maintain and scale.
GenAI can then automatically create test cases by interpreting user stories and converting them into clear, executable steps. A monitoring layer can help provide visibility through detailed logs, event tracking, and error reporting. AI-driven features enable tests to self-correct when issues arise and continuously learn from past results. An evaluation component reviews test quality, identifies gaps, and removes low-value cases. Going forward, a planning agent will prioritise tests based on risk, business impact, and recent code changes, ensuring faster and more reliable software delivery.
Intelligence and adaptability
Agentic AI-based test automation brings intelligence and adaptability to omnichannel retail systems by autonomously identifying, executing, and improving test scenarios across web, mobile, and in-store platforms. It reduces manual effort, speeds up release cycles, and ensures consistent performance across all customer touchpoints. For retailers, this means faster innovation, fewer errors, and smoother integration between online and offline channels. For consumers, it translates into a seamless, reliable shopping experience—whether browsing on an app, purchasing online, or picking up in-store—ultimately boosting satisfaction and brand loyalty. Key benefits include:
- Expanded test coverage through dynamic, automated test generation
- Reduced maintenance costs via self-healing and adaptive logic
- Context-aware testing that aligns with application objectives
- Continuous improvement enabled by feedback and learning loops
- Enhanced issue diagnosis through autonomous evaluator agents
- Immediate test feedback for developers, resulting in more stable continuous integration (CI), continuous deployment (-CD) pipelines
- Quality analysis (QA) teams can prioritise exploratory testing while agents manage regression tasks
- Product managers achieve consistent quality across features with less manual oversight
- DevOps engineers can scale and trigger tests efficiently based on environment and usage patterns
- Business leaders benefit from lower QA costs, accelerated release cycles, and increased customer satisfaction
Reliable omnichannel
Adaptive agentic AI promises to revolutionise test automation in the omnichannel retail and will help ensure flawless, consistent, and personalised customer experiences across all channels by intelligently detecting issues, learning from user interactions, and continuously optimising system performance with minimal human intervention.
By replacing brittle, reactive scripts with self-adaptive, intelligent agents, it offers intelligence, adaptability, and autonomy to testing operations, which can help retailers rapidly detect issues, maintain quality across complex digital and physical touchpoints, reduce testing costs, and deliver a smoother, more reliable omnichannel experience for customers. Additionally, this approach aligns with the industry's demand for speed, reliability, innovation, resilience, and superior customer experiences. With rapid AI advancements and increasing quality assurance demands, retailers need to embark on the agentic transformation journey to maintain competitiveness in an experience-driven market.