Products and Platforms
Highlights
- Enterprise customers in the telecom sector demand tailor-made solutions with hyper-personalised services, pricing, and proactive support.
- Gen AI, with its ability to create content, automate interactions, and generate insights, offers a powerful technology to transform B2B customers' experience.
- The paper reimagines the B2B Telco sales process through the lens of enterprise architecture, value chain analysis, and capability modelling, offering a blueprint for Gen AI-powered transformation.
On this page
Context
Enterprise customers expect hyper-personalised solutions, flexible pricing, and proactive support. Yet, current systems struggle with these demands, and long quote-to-order cycles add cost and delay even before core services are delivered.
According to Gartner® B2B Buying Report: “Seventy-five percent of B2B buyers say they prefer a rep-free sales experience, but self-service digital commerce purchases are significantly more likely to result in purchase regret.” Gen AI can accelerate this shift by creating content, automating interactions, and generating insights.
This paper reimagines the B2B telco sales process through the lens of enterprise architecture, value chain analysis, and capability modeling—offering a blueprint for AI-powered transformation.
Architecture vision
The architecture vision aligns with the service provider’s strategic goals to enhance B2B customer experience, reduce manual processes, and shorten sales cycles. The goal is to build a scalable, intelligent, and secure enterprise architecture that automates workflows, personalises customer interactions, and accelerates business outcomes. The table below outlines key business drivers, KPIs, and target improvements, highlighting where GenAI can deliver measurable impact.
| Business driver | KPI | Baseline | Target | Remarks |
| Customer experience and engagement | Customer satisfaction score (CSAT) | 75% | 90% | Post-AI chatbot deployment |
| Net promoter score (NPS) | 30 | 50 | After personalised AI interactions | |
| AI-driven interaction rate | <10% | >50% | % of support handled by AI | |
| Response time reduction | Avg. time reduced from two hours to 30 mins |
| Sales cycle optimisation | Sales cycle duration | 45 days | 15 days | AI-assisted lead qualification |
| Proposal generation time | 3 days | 1 hour | Using generative AI templates | |
| Lead conversion rate | 15% | 30% | AI scoring and personalisation | |
| AI-assisted deal win rate | 40% | % of deals influenced by AI insights |
| Operational efficiency | Process automation rate | 25% | 70% | Across sales, support, and provisioning |
| Cost-to-serve reduction | 30% | Reduced manual effort and errors | ||
| Error rate in manual processes | 15% | <5% | AI AI validation and automation |
Figure 1: Business drivers and KPIs (Illustrative)
Business architecture
- As-is business architecture
The “As-Is” architecture represents the current state of how the organisation operates within its ecosystem. It serves as the baseline for analysis, helping us understand existing business processes and identify which areas could be impacted by the introduction of Gen AI as part of the transformation.
- To-be business architecture
In the to-be business architecture, the impacted processes that are considered for the proposed Gen AI solution are –
| Impacted business process | Gen AI solution |
| Market sales readiness and support (Selling) | Conversational AI customer support |
| Customer support management (Cross-sell/upsell) | Personalised product recommendations |
| Fulfilment (Negotiate sales/contract) | Automated quote generation Smart contracts |
Below are the impacted journeys in the identified business processes:
- Lead-to-order: Automate lead qualification and proposal creation
- Order-to-cash: Streamline order processing and invoicing
- Customer support: Deploy AI chatbots for tier-1 support
- Product lifecycle management: Use AI for feature ideation and documentation
Value stream mapping
To identify where to integrate Gen AI effectively, organisations must identify high-impact areas where it can reduce manual work and enhance the overall customer experience. Value stream mapping highlights the business activities best suited for AI infusion.
Challenge areas: Enterprise customers typically engage across multiple touchpoints. These journeys are often manual and involve lengthy coordination. Gen AI can address these challenges by adding conversational interfaces, providing data-driven insights, and automating critical steps across stages.
These journeys involve lengthy coordination, mostly manual and people dependent. Gen AI can address these challenges by infusing conversational interface support, data insights, and automating steps across the stages.
| Value stream step | Key activities | Stakeholders | Bottlenecks | Gen AI opportunities |
| Lead identification | Market segmentation, targeting, and prospecting | Sales, Marketing | Manual data entry, slow lead qualification | Automated scoring of prospects, predictive lead generation |
| Opportunity qualification | Needs analysis, solution fit, stakeholder mapping | Sales reps, Solution architects | Redundant data collection, fragmented customer insights | Unified customer profiling, Product recommendations |
| Solution design | Product bundling, technical design, and pricing options | Pre-sales, engineering | Manual configuration, pricing errors | Dynamic pricing engines, AI-assisted configuration |
| Quote creation | Proposal drafting, approvals, and legal checks | Sales ops, legal, finance | Extended approval cycles, policy compliance gaps | Automated document generation, AI-based legal review |
| Order submission | Order validation, system entry, customer communication | Order management, customer care | Manual input, duplicate entries, slow notifications | Automated order capture, real-time status updates |
| Fulfilment and activation | Resource provisioning, service activation, and billing setup | Operations, IT, billing | Legacy system delays, handoff errors | Intelligent workflow orchestration, predictive resource allocation |
Figure 2: Value stream mapping
Gen AI implementation
Application architecture
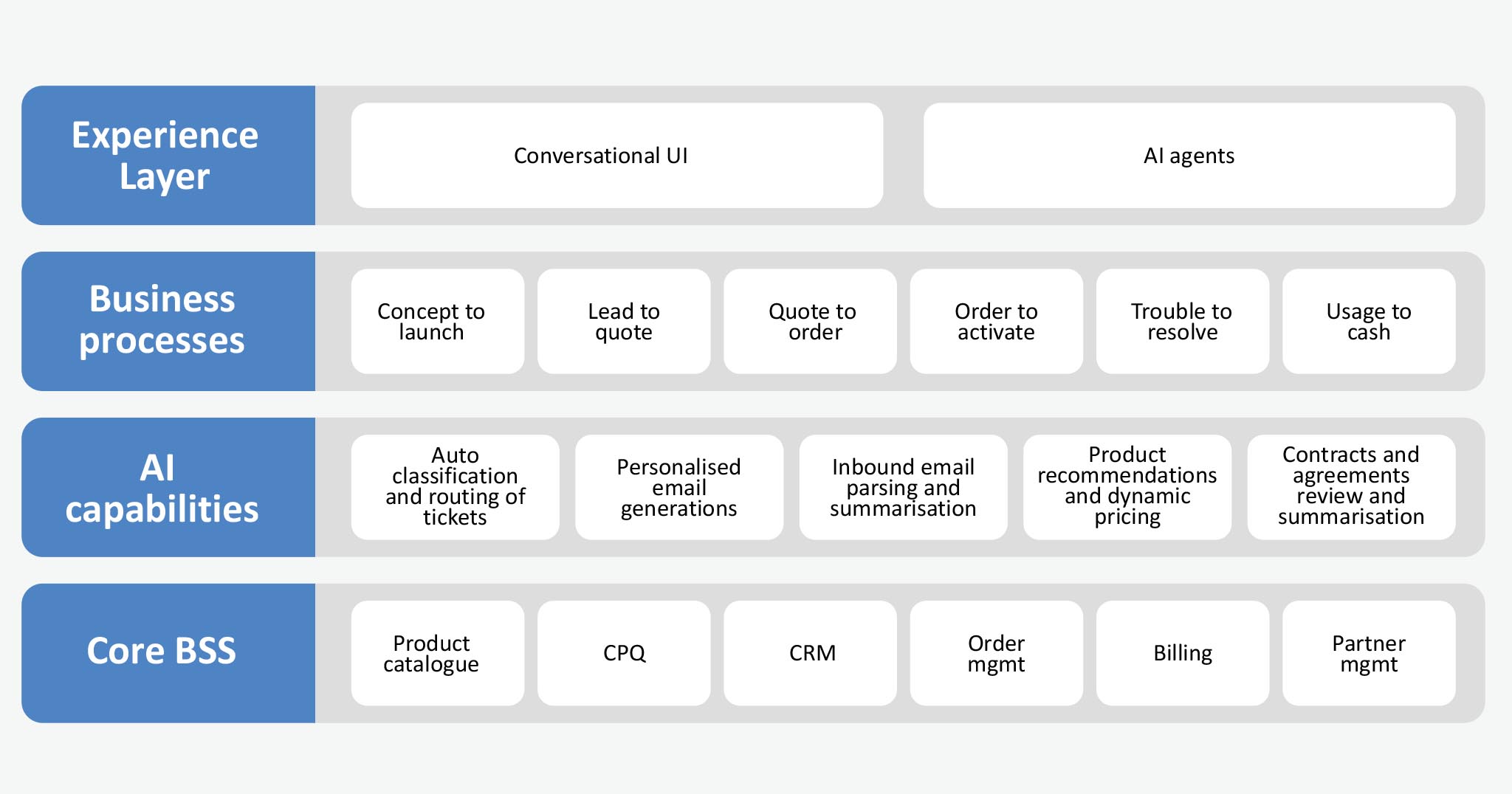
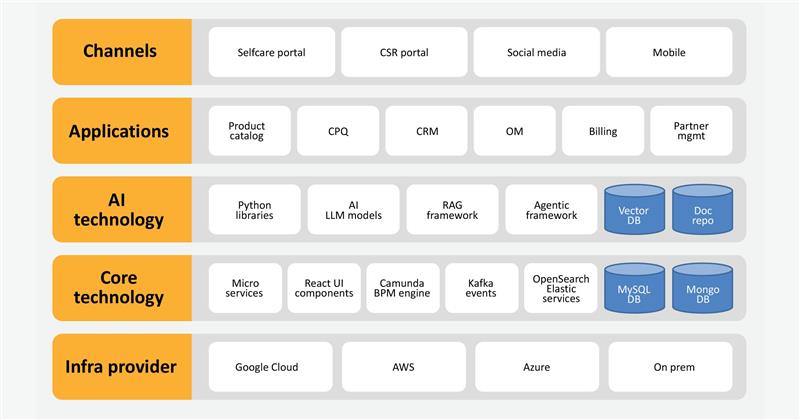
Gen AI can transform core telco applications by making CPQ smarter with automated quoting and lead scoring, enriching CRM with personalised recommendations and seamless journeys, and strengthening the product catalogue with product ideation, offer ability insights, and compliance checks. Customer support is enhanced through AI-powered virtual agents, while an API-first, microservices-based integration ensures scalability and interoperability.
AI success depends on strong data foundations. Customer interactions, sales history, and product data must flow into a centralised data lake, governed by metadata, lineage tracking, and quality controls.
On the technology side, cloud-native platforms with GPU-enabled clusters, scalable storage, and networking support advanced workloads. An AI/ML stack with generative models, MLOps pipelines, and monitoring tools ensures agility, while security, compliance, and ethics are embedded through access controls, encryption, and bias monitoring.
Opportunities and solutions
- Smart sales engagement: Faster quotes, self-service, and personalised customer outreach.
- Offer and solution management: AI-driven recommendations, dynamic pricing, and bundling.
- Order and fulfilment: Automated orchestration across front and back office.
- Legal and compliance: AI-enabled contract review, risk detection, and summarisation.
- Performance analytics: Real-time KPI tracking, renewals, and upsell guidance.
- Proactive support: Automated case handling, classification, and virtual agent support.
Migration planning
To successfully deliver the transformation objectives and enable a smooth journey from legacy systems and manual processes to AI-enabled operations, the following migration principles must be adopted:
- Business value first: Focus on use cases with measurable impact and align all AI initiatives with strategic KPIs.
- Data readiness and quality: Ensure data is clean, structured, and accessible while maintaining governance for lineage, privacy, and compliance.
- Incremental and agile rollout: Start with pilots, scale gradually, and use agile methods to refine AI models.
- Interoperability and modularity: Design AI as microservices and ensure compatibility with existing CRM, ERP, and support platforms.
- Security and compliance by design: Embed security controls into workflows and comply with telecom regulations and data protection laws.
| Risk category | Potential risks | Mitigation strategies |
| Data | Poor data quality, privacy breaches | Data audits, anonymisation, and governance policies |
| Model | AI hallucinations, bias, and low accuracy | Model validation, human-in-the-loop, continuous retraining |
| Operational | Downtime during migration, integration failures | Parallel runs, rollback plans, phased deployment |
| Security | Unauthorised access, model misuse | Role-based access, encryption, and monitoring |
| Compliance | Violation of telecom/data laws | Legal reviews, compliance automation, audit trails |
| Adoption | Low employee or customer usage | Training programs, feedback loops, and UX optimisation |
| Financial | Cost overruns, unclear ROI | KPI tracking, cost-benefit analysis, governance checkpoints |
Figure 5: Migration risks and mitigations
Implementation roadmap
| Phase | Key activities | Timeline | Responsible teams |
| Strategy and vision | Define transformation goals, align with business priorities, and secure sponsorship | Q1 | CIO office, strategy team |
| Use case identification | Identify high-impact B2B scenarios, prioritise use cases | Q1 | Enterprise architecture, Business units |
| Infrastructure and data readiness | Set up cloud infrastructure, ensure data governance, and integrate systems | Q2 | IT operations, data engineering, security and compliance |
| Pilot programs | Launch controlled pilots, measure outcomes, gather feedback | Q3-Q4 | AI team, business units, change management |
| Full-scale deployment | Expand successful pilots, integrate AI into enterprise systems, and manage changes | Q3-Q4 | IT delivery, business units, training and enablement |
| Continuous optimisation | Monitor KPIs, refine models, and evolve use cases based on feedback | Q4 and beyond | AI team, enterprise architecture, governance committees |
Figure 6: Implementation roadmap (Illustrative)
Implementation governance
AI governance begins with architecture compliance, ensuring models follow approved design patterns and integrate with systems like CPQ, CRM, and support platforms through modular, API-first approaches. Compliance checklists covering explainability, output validation, and data privacy (e.g., PII masking) reinforce security. At the same time, monitoring protects against prompt injection and ensures adherence to telecom rules and frameworks such as the EU AI Act.
Responsible governance is led by an ethics and risk committee that defines acceptable use, manages hallucination controls, and enforces human-in-the-loop processes. Model lifecycle management is handled through MLOps pipelines to track versioning, retraining schedules, and output accuracy. Performance is aligned with CIO-level KPIs such as proposal turnaround time, AI-driven interaction rates, and lead conversion uplift monitored through real-time dashboards.
Change and exception management rely on impact analysis and rollback procedures for safe updates. Finally, stakeholder engagement is enabled through prompt libraries, decision logs, AI literacy workshops, user feedback loops, and customer advisory boards, which drive accountability and continuous improvement.
Architecture change management
AI change management ensures updates, whether model retraining, prompt adjustments, integrations, or compliance shifts are introduced responsibly. Changes are classified as minor (tweaks), major (model replacement), or emergency (hallucination fixes) and assessed for business impact, KPIs, and compliance. Governance bodies like the Architecture Review Board, AI Ethics and Risk Committee, and Data Governance Council approve changes based on principles, risk plans, and measurable outcomes.
To safeguard performance, versioning tracks models, prompts, and APIs through repositories and audit logs, while rollback plans manage faulty deployments with backups and test environments. Effective communication keeps teams informed with documentation, training, and dashboards. Finally, continuous user feedback and performance metrics feed into retraining and refinements, ensuring AI evolves in line with business needs.
Conclusion
By embedding GenAI into customer engagement, sales, and operations, telecom providers can cut sales cycles, speed up deal closure, ease account manager workloads, and deliver a smoother enterprise customer experience. Guided by a clear architecture, governance, and implementation roadmap and with responsible AI and data integrity at the core, the approach is built to be scalable, secure, and future-ready.