Industry
Highlights
- The authenticity of educational credentials is increasingly under threat amid an environment where degrees can be easily forged, diplomas can be faked, and certifications overstated.
- Typically, students' academic data is distributed and it is often observed that when students move between countries, schools, or apply for jobs, the process becomes slow, bureaucratic, and vulnerable to errors.
- Poor organizational workflow impacts data duplication and inconsistency. A lack of transparency creates trust issues between divisions, vendors, partners or even within large education service providers.
- Today, organizations store data in different formats, which leads to issues arising from data silos and lack of interoperability.
On this page
Theory into Practice
Evolution from a scattered system to a transparent, secure, and overall effective management system would ensure efficient redeployment of academic history that can be shielded from manipulation.
The primary aim of higher education institutions is to use technology like blockchain to secure, manage, store, and verify educational manuscripts, records, and other relevant data. Creating a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger blockchain must ensure the genuineness and truthfulness of information, making it perfect for various applications such as issuing degrees, managing student records, academic scores, project details and confirming qualifications across institutions.
Going from an idea to the execution considers the following benefits:
- Uniform data formats: Blockchain nurtures the use of universal schemas for storing and sharing information. For example, all student records, certificates, or encrypted transactions follows a universal format across the network.
- Interoperable systems: Blockchain networks (especially enterprise blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric, Corda) are built to interoperate across different enterprises and platforms. Data written once can be accessed universally by an authorized participant.
- Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) for students: Students’ specific digital identity on blockchain is private and secure. Their credentials (diplomas, degree, certificates, badges, skills) are linked to their identity, not to a school’s private server. Students can control who views what. Using cryptographic keys, students or certificates holders can grant or revoke access to specific parts of their record (for employers, corporates, universities, verification agencies etc.)
- Single Source of Integrity (SSOI): Blockchain acts as one shared, immutable ledger. All interested parties can see the same real-time data at the same time without any system glitch. This reduces multiple back-and-forth emails, approvals, thereby avoiding confusion. Every credential such as student documents relating to courses, projects and awards is completely digitally recorded on a blockchain. It turns into a single, verifiable, lifelong academic portfolio for the students.
- Decentralized metadata registries: Blockchain can hold the documents’ metadata like format, structure, version and credentials, enabling systems to understand and integrate foreign datasets automatically. All credentials are absolute and globally verifiable.
- Smart contracts enforce consistency: Smart contracts confirm that any information entered follows predefined formats, rules, and standards before accepting it into the blockchain. This can help avoid paperwork delays when students apply for validating any credentials globally.
The conventional education system requires multiple signatures and stamps to ensure accuracy, which can be time-consuming. Blockchain for education offers the preference to assess the grades of students across all subjects and excludes the need for manual processes. Since credentials are stored in a distributed ledger system, there is no intermediary to verify academic records such as certificates, degrees, diplomas etc.
The credentials can be obtained with a few web-based clicks. These clicks represent actions a user (students, institute, or employer) takes through a web-based application that interacts with a Blockchain based credentialing system.
The primary goal of implementing blockchain application in the education industry is to save data securely in the form of a chain. After it’s stored, the data is inaccessible to be changed manually because the latest encryption secures it.
Bridging Realities
Immersive blockchain technologies are emerging as a solution, offering more practical and real-world experiences.
Blockchains can create unique digital assets that verify the authenticity of academic qualifications and credentials. There are many other blockchain applications in the education industry and employment sectors and certification verification. Let’s look at these practical use cases of blockchain:
| Business Area | Use Case | Description | Benefits |
| Credentialing, authorization and authentication |
|
Higher educational institutions manage huge amounts of sensitive student information. One of the use cases of blockchain in education includes storing this data, with the promise of security and protection. Blockchain can be used to securely store and manage student records in a decentralized way. |
|
| Smart contracts & DApps |
|
Smart contracts and self-executing agreements with defined rules and conditions can simplify administrative processes within educational institutions. For instance, smart contracts development blockchain technology can automate procedures like student fee enrolment, fee payment, and grade calculation. |
|
| Regulation | Copyright protection for educational content | Stealing within the academic community is a major problem. The time invested could be lost if a research article is stolen or copied. A stolen assignment can cause low grades. Blockchain-based solutions can control the way copyrighted material is shared. | Increases data security and reduces data silos. |
| Faculty and staff /student attendance rates |
|
Monitoring teacher/students and staff performance is essential for improving the quality of education. Blockchain for education can offer unalterable evidence of teacher evaluations based on peer reviews and student/faculty feedback. Higher education services providers can easily access this information to conduct reviews of teacher performance, professional development, and promotions. |
|
Table 1
Assessing blockchain readiness
Scalability, reliability, and security are key to blockchain adoption in higher education, prompting institutions to evaluate their readiness for a decentralized future.
As in the case of other digital technologies, the critical criteria for mainstream blockchain deployment are scalability, reliability, and security. The most important question faced by the higher education service providers are whether their business is set to grow in a decentralized world or not. This, and some other questions listed in Table 2 would help the organizations assess their readiness for Blockchain deployment.
| Measures | Business readiness | Technology readiness |
| Conceptual judgement | Is the business ready to work with decentralized business models at a conceptual level? | Does the educational institute understand the challenges of blockchain's interplay with other legacy technologies? |
| Managerial backing | Is there full deliberate alignment and support from the entire CxO and each line of business? | Does the educational institute possess a deep understanding of its data capabilities and architecture? |
| Roadmap for technology and business | Has the educational Institute defined an implementation roadmap with a strategy arranged in a risk balanced portfolio of initiatives? | Has the educational institute developed blockchain architecture integration frameworks and tools to minimize disruption? |
| Business agility | Does the educational Institute have significant innovation maturity, including a lean start-up culture and relevant processes? | Is the educational institute actively engaged in technology-centric consortia and collaboration with start-ups? |
| Market overview | Does the organization have in-depth insights into the customer, partner, regulator, and start-up ecosystems in the marketplace and their value exchanges and associated requirements? | Can the organization run multiple Blockchain assembles that are abstracted from legacy systems? |
From concept to deployment
From securing digital assets to safeguarding academic achievements, blockchain technology is making significant mark far beyond the educational sector.
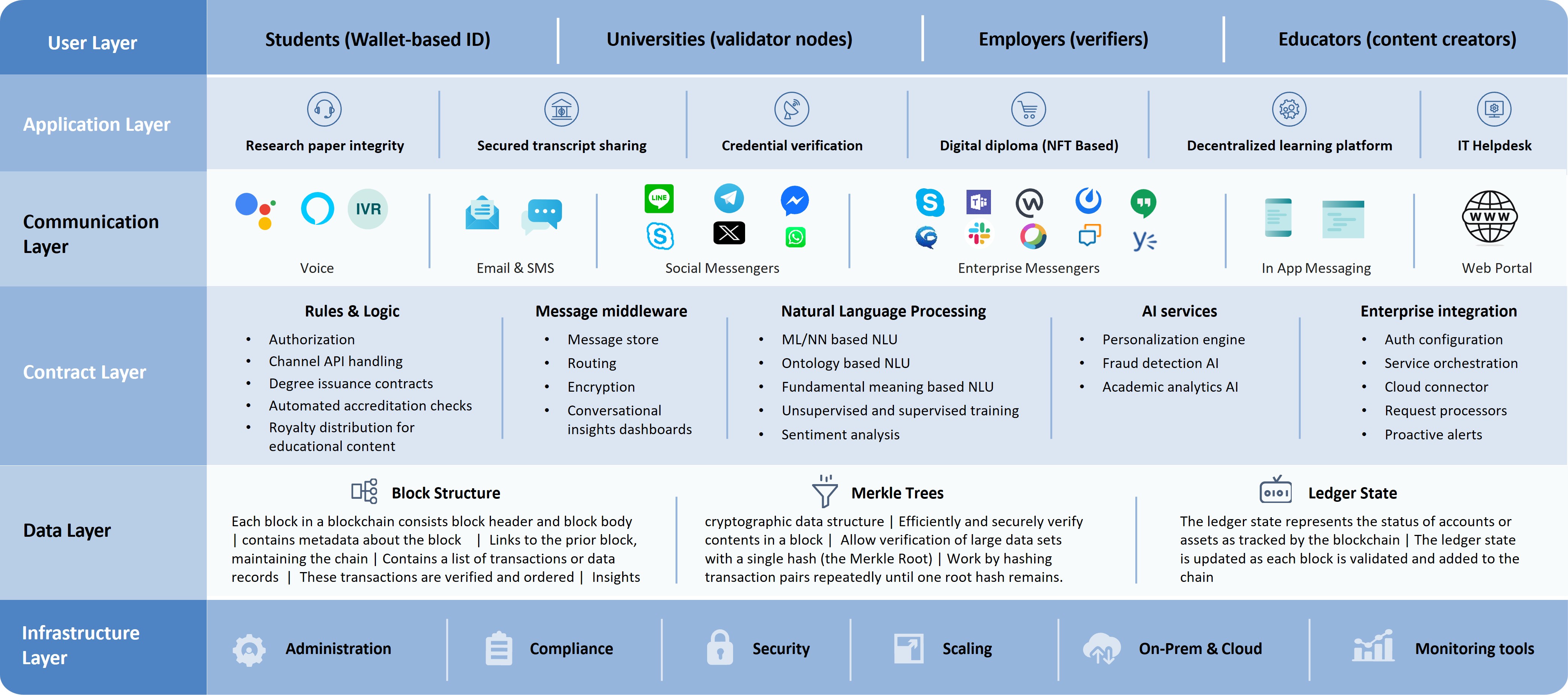
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that allows multiple participants to record transactions in a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way without the need for a trusted central authority. The architecture design of a blockchain determines its performance, scalability, security, and interoperability.
Emerging trends in blockchain architecture:
- Modular blockchains: Separation of consensus, data availability, and execution layers (e.g., Celestia).
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS): Managed blockchain hosting (e.g., Azure, AWS, IBM).
- Decentralized Identity (DID) is a blockchain-based system that allows individuals and organizations to own, control, and verify their identity without relying on central authorities like governments, universities, or corporations.
- Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT): Blockchain as a secure backend for AI-driven decision systems and IoT devices.
- Quantum-Resistant Blockchains: Preparing for post-quantum cryptography needs.
Developing a blockchain execution plan for a higher educational enterprise.
The best strategy for blockchain adoption is to start small with use cases (like issuing blockchain-backed digital certificates, and records and verifying academic transcripts on the blockchain, issuing a digital student ID and storing key academic records securely on-chain etc.) that offer promising potential. This helps higher education services providers assess their readiness for blockchain deployment, clearly identifies functional areas where blockchain can drive faster value and delineates a roadmap for its adoption.
Next steps for blockchain in higher education
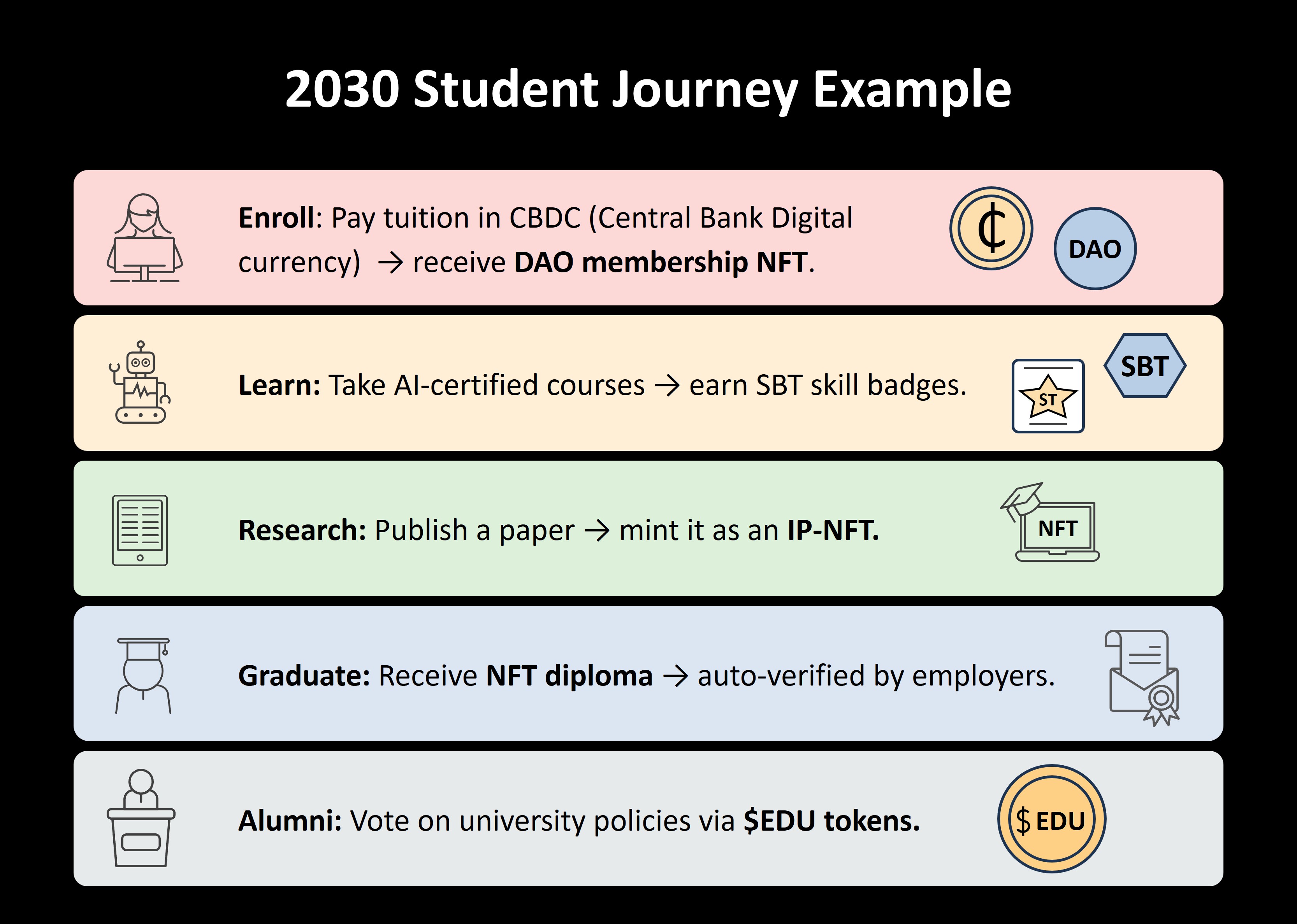
Blockchain will revolutionize higher education into a student-centric, borderless, and skill-verified ecosystem.
Here’s how:
Lifetime digital diplomas:
- Degrees are issued as Soulbound Tokens (SBTs) on Ethereum/Polygon.
- Establishments verify instantly via QR scans (no more transcript requests).
Micro-credentials:
- Skills (e.g., Python, CRISPR editing) are tokenized as NFT badges.
- Stackable into "degree NFTs."
Global skill passport:
- All degrees/certificates are NFT-based and AI-verified.
- AI career advisors match your on-chain credentials to jobs.
- Tokenized voting: Students, alumni, and faculty govern universities via governance tokens (e.g., $EDU).
- Vote on curriculum updates, research funding, and tuition policies.
- Transparent budgets: All university finances are on-chain (e.g., endowment funds, salaries).
- Example: "MIT’s DAO votes to allocate 20% of its budget to AI research."
Blockchain as the universal registrar:
- A W3C-standardized ledger replaces regional accreditation bodies.
- Smart contracts auto-convert credentials across borders (e.g., Indian MBA → EU-recognized).
AI-Powered job matching:
LinkedIn 3.0 uses on-chain credentials to auto-suggest careers.
Peer-to-Peer education marketplaces:
- Professors tokenize courses; students pay with crypto.
- Example: "A Stanford prof sells ‘Quantum Computing 101’ as an NFT course."
Learn-to-Earn (L2E):
Students earn tokens for completing modules (e.g., $MATH for math courses).
Patent NFTs:
Researchers mint patents as NFTs, enabling royalty streams via smart contracts.
Decentralized peer review:
Scientists earn tokens for peer-reviewing papers (no more paywalled journals)
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI):
- Students own their data via DID wallets (e.g., Polygon ID).
- Share only what’s needed (e.g., prove you’re a student without revealing grades).
- Self-sovereign identities with AI tutors guiding personalized learning journeys.
For CIOs, IT directors, CFO and functional leaders of higher education services providers, blockchain is a strategic lever to drive efficiency, trust, and innovation in education. By starting with targeted pilots, collaborating across stakeholders, and integrating AI, institutions can position themselves as leaders in the digital education era. The future of education is decentralized—and the time to act is now.
Call to Action:
- Conduct a blockchain readiness assessment.
- Assess needs: Identify pain points (e.g., slow credential verification).
- Pilot use cases: Start with narrow applications (e.g., Academic digital transcripts).
- Collaborate: Partner with EdTech blockchain providers (e.g., Learning Machine, Hyland Credentials, Education IT Service Providers).
- Partner with a trusted blockchain provider.
- Secure stakeholders buy-in through demonstrable ROI.
Blockchain holds the key to a more secure, efficient, and equitable education system. By overcoming challenges through practical strategies, and by integrating AI, institutions can future-proof their operations and amplify educational outcomes. The time to act is now, and the roadmap is ready for adoption.