Industry
HIGHLIGHTS
- Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform the recruitment landscape by enabling efficient processes such as automated resume screening and AI-driven candidate engagement.
- AI can cut recruitment time by 50%, reduce hiring costs, ensure bias-free recruitment, and enhance access to relevant candidates.
- To successfully adopt AI, staffing and recruirment companies must define a clear roadmap and choose the right AI architecture.
On this page
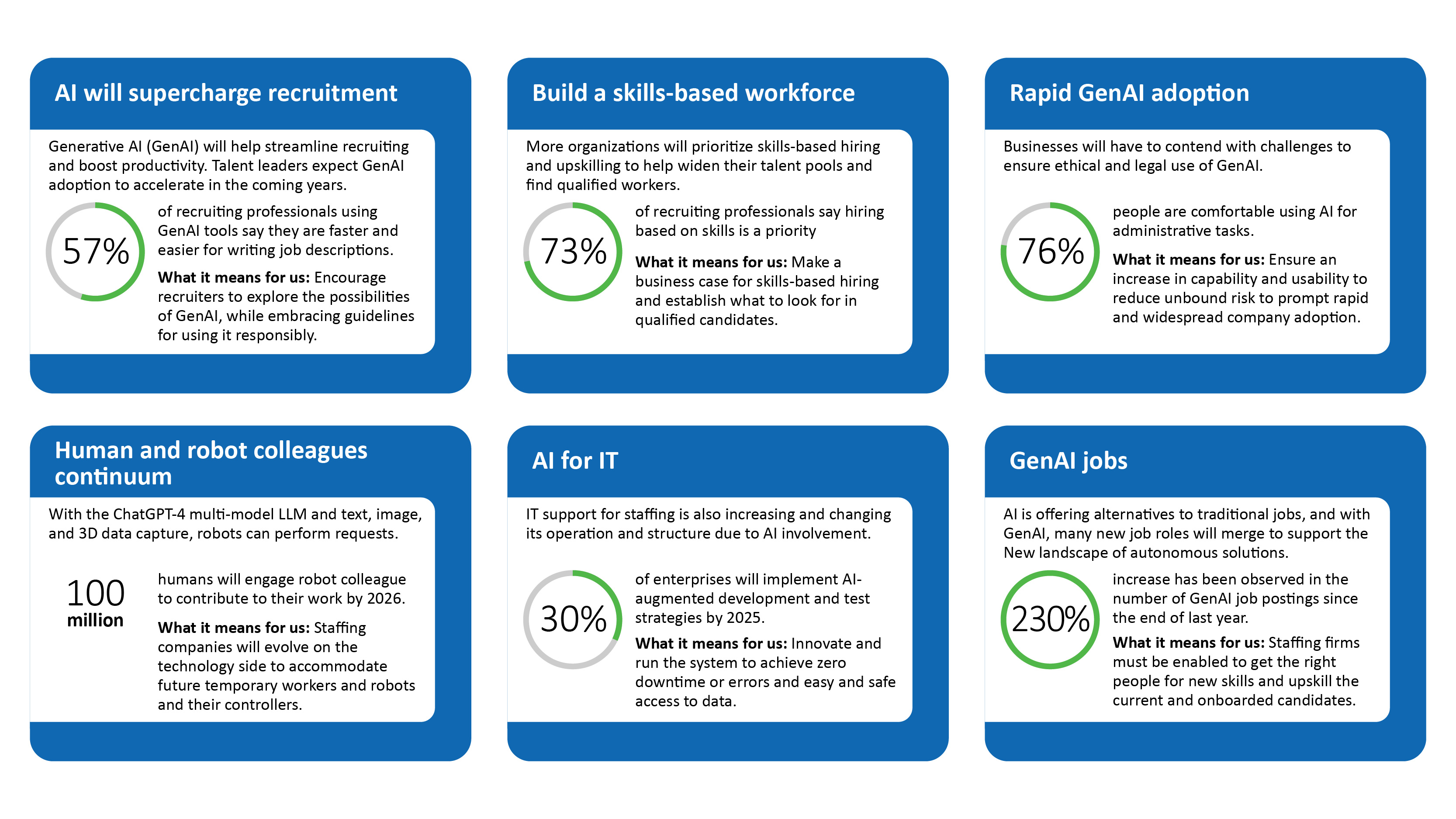
Emerging trends in the staffing and recruitment industry
The staffing and recruitment industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and changing workforce dynamics.
As organizations strive to attract and retain top talent, new strategies and trends are shaping the future of recruitment Emerging technologies such as generative AI (GenAI) are projected to generate US$ 2.6 trillion to US$ 4.4 trillion of economic value annually by 2028, which will also revolutionize hiring processes across industries.
AI is not only accelerating job matching and automating repetitive tasks, but also redefining workforce strategies. From automated resume screening to AI-driven candidate engagement, the recruitment landscape is rapidly evolving to accommodate the losses and gains of AI transformation. We explore key market trends in the staffing and recruitment industry, AI disruptions, and strategic recommendations for companies to shape the future of staffing.
Key trends transforming the staffing and recruitment industry include:
Renewed tech stack: Companies are investing heavily in automation and AI-driven solutions to optimize back-office operations and sourcing strategies. They are also exploring mechanisms to automate human touch points using AI. AI is expected to enhance productivity in hiring workflows. 40% of enterprise applications will feature embedded conversational AI to streamline candidate interactions. Regulatory frameworks are being developed to manage data autonomy, which will enforce ethical AI usage in hiring. Digital transformation is enabling seamless hiring experiences, reducing the time to hire, and improving overall process efficiency.
Emergence of multi-platform solutions: Organizations are moving toward integrated staffing platforms that offer a broad range of employee-related services under a single umbrella. These platforms provide customized solutions, replacing standalone HR applications for a more cohesive hiring experience.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) priorities: ESG compliance is becoming a key consideration in corporate hiring policies. Companies are leveraging financial incentives for sustainability reporting, which enhances employer branding. Investors and customers are increasingly favoring businesses with strong ESG compliance in workforce management.
Cross-industry disruption from tech giants: Non-traditional players such as Amazon, X (formerly Twitter), and leading consulting firms are entering the talent acquisition space. These companies leverage their strong technological infrastructure to disrupt traditional recruitment practices. AI-powered talent marketplaces are challenging conventional staffing models by offering direct employer-to-candidate connections.
A booming market, but with its challenges
The AI market is rapidly expanding, opening up new avenues for growth across industries.
Despite increasing interest in this technology, organizations across industries are facing challenges in adopting AI. Firstly, the cost of AI resources is particularly high and there is a growing demand for flexible work models. Secondly, given that it is still an evolving technology, there are visible skill gaps leading to unfilled vacancies across organizations. If we talk specifically about the recruitment industry, there delay in adoption and implementation of AI due to the lack of relevant use cases that would make the case for AI-driven efficiencies.
In our interactions with industry leaders, we have learnt that AI-driven automation can bring about a significant reduction in human-serviced contacts, leading to a shift in how human resources (HR) professionals engage with talent.
There are growing concerns about the job displacement that AI will cause. For instance, we anticipate a decline in traditional clerical roles, with commercial staffing sectors (such as back-office and clerical jobs) expected to decline Despite resilience in industrial roles, AI will accelerate job displacement in administrative and routine functions and drive transformation in specialized job functions. Nearly two-thirds of specialist roles across industries will see some degree of automation or modification, requiring employees to adapt to new digital tools and AI-integrated workflows. Business functions across various industries will require a shift in job roles and skill sets, leading to increased demand for hybrid skill profiles.
But all is not bleak and gloomy, with AI presenting a host of career transition and upskilling opportunities. The need for reskilling and upskilling will grow as AI-led automation changes traditional career paths. Going by early trends in this regard, we expect millions of occupational shifts over the next few years, emphasizing transferable skills and continuous learning to bridge talent shortages.
Figure 1 is a quick summary of the disruptions AI, particularly GenAI, is set to cause in the staffing and recruitment space.
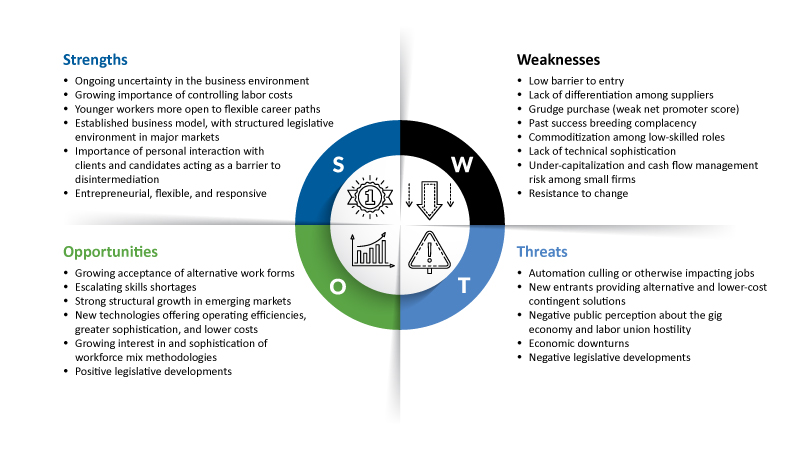
A SWOT analysis of the staffing industry
Adopting AI in staffing comes with certain challenges, but it also presents opportunities across functions for staffing firms.
In Figure 2, we present a comprehensive SWOT analysis of the staffing industry.
Staffing firms have the opportunity to accelerate hiring by enhancing candidate experience, boosting productivity, and ensuring accuracy. However, to fully capitalize on AI-driven solutions, they must first address key challenges such as job displacement risks, potential hiring biases and compliance with labour laws. Overcoming these hurdles will enable firms to integrate AI responsibly, unlocking its full potential while maintaining fairness, transparency and regulatory alignment
- Job displacement risks: Automation could eliminate clerical and administrative jobs in recruitment.
- AI bias and ethics: AI models, if not properly trained, can amplify hiring biases. Ensuring ethical AI use requires careful oversight and unbiased training data
- Compliance and data privacy: AI-driven hiring must comply with labor laws and data regulations.
That said, opportunities galore; some interesting ones to watch out for are:
- Enhanced hiring efficiency: AI can cut recruitment time by 50%, improving speed and accuracy.
- Cost saving: AI-led automation can reduce hiring costs by eliminating manual tasks.
- Improved diversity and inclusion: When implemented correctly with bias-mitigation strategies, AI-powered hiring can support fair recruitment based on skills rather than subjective factors.
- Improved customer access: AI can enhance access to relevant candidates and enable touchless interaction.
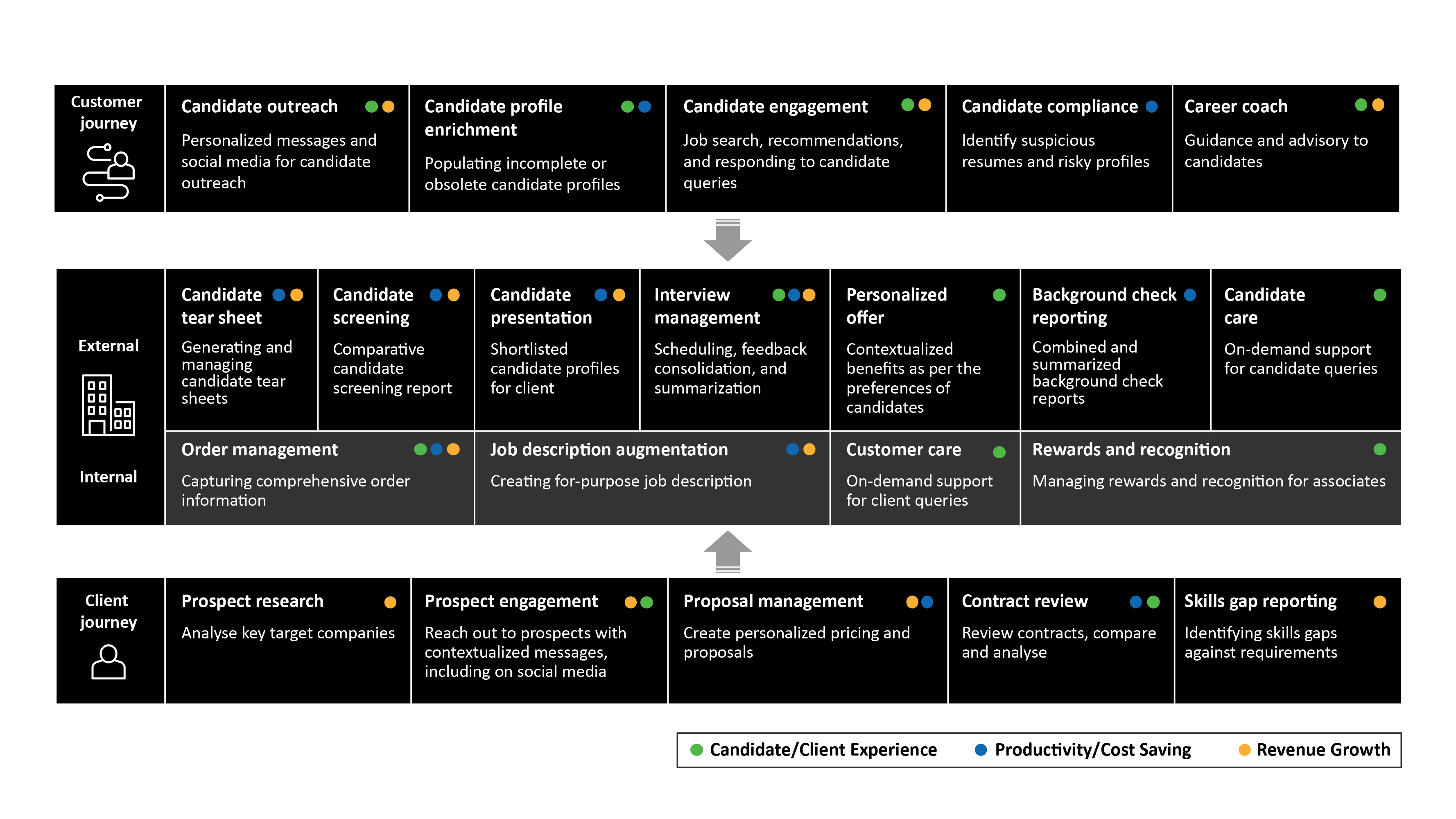
Generative AI use cases across the staffing value chain
With GenAI, staffing and recruitment firms can enhance the candidate experience while improving operational efficiency.
GenAI can be leveraged for a number of use cases in staffing (see Figure 3). It can optimize employee and customer interactions, support clients in streamlining requisition tracking, and provide seamless access to candidate profiles and status updates. AI can help organizations makes informed decisions on budgeting and resource allocation and adopt data- driven and user-centric recruitment processes.
Table 1 shows the integrated use cases for the candidate journey.
Value Chain |
Candidate |
Recruiter |
| Touch Points | Office/Industrial/ professioanl
|
Upsell, crosssell & operations
|
| Candidate Outreach | Resume builder, New role of monitoring and prompt engineering, commanding robots will evolve
|
Personalized/ Customized Outreach messages,Content creation for Outreach campaigns, scoial profiling for the candidate and feedback collection and analysis
|
| Candidate Profile Enrichment | Simulate interview scenarios based on the response of the candidate for interview preparation
|
Resume summarization of right candidates Create personalized job description
|
| Candidate Engagement | Interactive Chat bot support Prescreening interaction through chat
|
Based on response rates and conversation rates, recommendation for optimizing future outreach roadmaps
|
| Candidate Compliance | Summarization of certificates or mandate need for the applied job so that they would be ready for BGC. Conversion of language to adapt to understanding of the official for faster processing.
|
W2 Payroll report generation, Feedback collection and summarization
|
| Career Coach | Human like interface to guide on career path, Assist learning in real time, answering question and providing explanations
|
Analyze program performance and provide instant feedback on assignment. Adapting difficulty to user adaptivity
|
Table 2 shows the integrated use cases for the client journey through a recruiter’s lens
Value Chain |
Client |
Recruiter |
| Touch Points | Hire manager
|
Up-sell and cross-sell & operations
|
| Prospect Research | Data analysis report generation through intractive chatbot
|
Guide through decision making process through suggestion backed by analytics
|
| Prospect engagement | Enhance the current website chatbot to gen AI chatbot to make query conversion more interactive reducing the need of emailing to the company.
|
Self Service Project creation & budget identification and allocation suggestion
|
| Proposal Management | Creation of first draft of contect based on intraction with similar vendor and market analysis & risk profiling of the vendor. Summarization of proposals best proposals
|
MoM and Transscript Generation. Presentation creation: Provide relevant research summary, prepare first draft from internal (enterprise) and external data
|
| Contract Review | Compare different versions of the contract and update the missing terms in the latest version .
|
Recommend changes to fulfil changes requested by client. Help gather insights to support claims in the contract
|
| Skill Gap Reporting | Indentify gap in skill and employees required in the current resourse portfolio
|
Suggest profiles to the gaps identified with summary insights for better decisioning on candidate
|
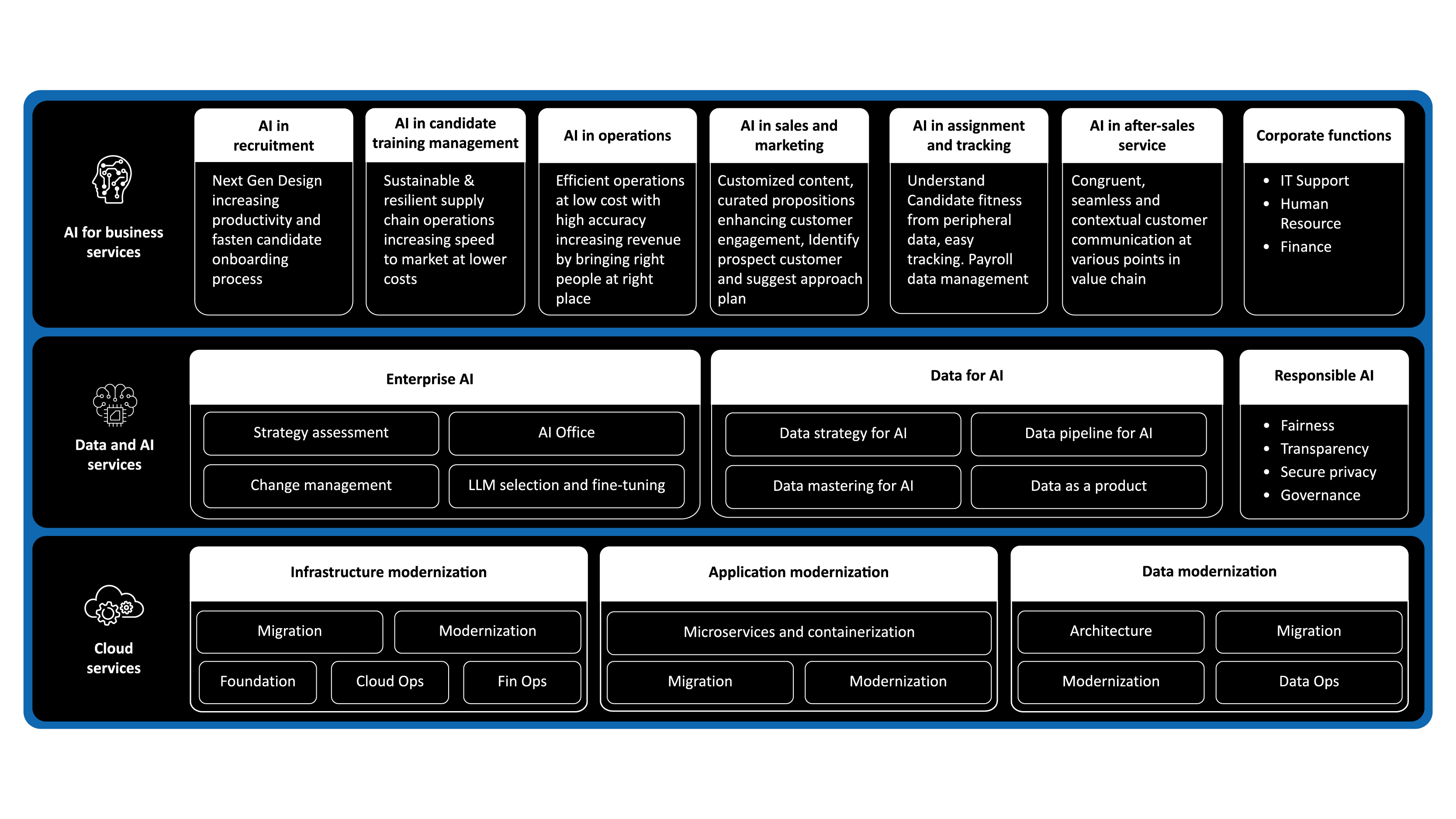
A roadmap for AI adoption in the staffing and recruitment industry
For successful AI implementation, staffing companies must weigh risks against opportunities and define a clear adoption roadmap.
They must use AI in the areas of business services, data services, and cloud and infrastructure services. This will help them intergrate data-driven insights and cloud technology to enhance operational efficiency, improve candidate experience, and streamline workforce management.
Figure 4 illustrates areas in which staffing and recruitment companies can adopt AI.
AI for business services: Companies can adopt AI in recruitment, candidate training, operations, sales and assignment tracking, and after sales services to improve workforce efficiency. It will enable faster candidate onboarding, workforce optimization, enhanced customer engagement, and seamless data management.
Data and AI services: AI can play a crucial role in strategy assessment, change management, large language model (LLM) selection, and fine tuning to improve the recruitment processes. Data- driven AI ensures better decision making through predictive analytics, talent insights, and process automation.
Cloud and infrastructure modernization: Cloud migration, modernization, and a microservices- based architecture can enable scalability, security, and efficiency in recruitment operations. AI- driven data pipelines, architecture modernization, and secure data management can ensure smooth and reliable recruitment operations.
Responsible AI: Companies should lay an emphasis on ethical AI practices, including fairness, transparency, security, and governance. This will ensure AI-driven recruitment processes are ethical, unbiased, and compliant with industry standards.
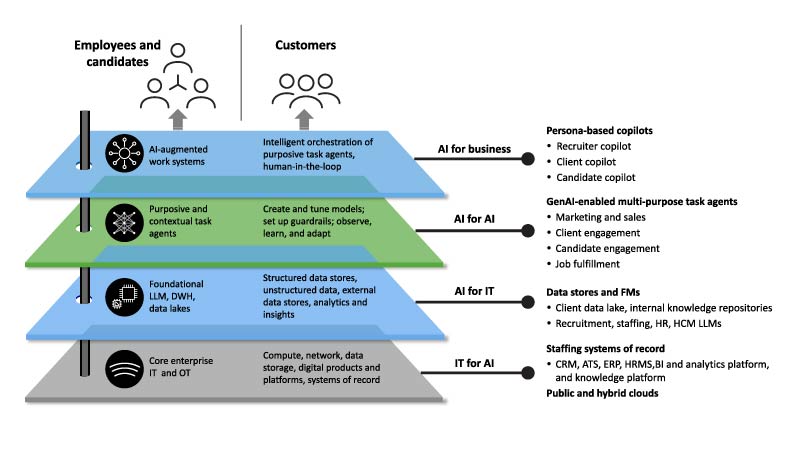
We propose an AI architecture for recruitment companies to build their AI capabilities on(see Figure 5), where different AI components collaborate with data and cloud technology. The architecture runs on a strong IT foundation, including cloud storage, digital tools, and secure data handling to support different layers of architectural AI capabilities for business and IT processes.
The top layer will help recruiters and hiring managers orchestrate and optimize tasks to make hiring smoother. The middle layers will observe, learn, and adapt to improve hiring by analyzing candidate profiles, resumes, and job market trends. The bottom layer will secure and scale the cloud platform to manage large amounts of hiring data.
The future of recruitment is AI driven
Recruitment firms must leverage AI to find the right candidates for their customers at the right time.
AI has the potential to make the recruitment process faster, smarter, and more efficient. It is more about understanding the clients’ thinking and their challenges more than just requirement gathering. With AI-driven automation and intelligent copilots, companies can transform hiring processes, reduce costs, and create an inclusive workforce.
But AI is not here to replace recruiters; it here to empower them. The future belongs to organizations that embrace AI responsibly, upskill their workforce, and adapt to the changing dynamics of hiring.