Industry
Highlights
- With data volumes skyrocketing in the automotive industry, the Sustainable Data Utility (SDU) Framework is critical to address growing energy demands, environmental concerns, and operational inefficiencies while ensuring actionable insights.
- Data is now the backbone of innovation in the automotive industry, yet its exponential growth brings significant sustainability challenges, including increased energy consumption, generation of e-waste, and unused data wastage.
- The SDU Framework introduces a strategic approach to data management, ensuring that data practices are purpose-driven, energy-efficient, and aligned with sustainability goals.
- By leveraging technologies like Zero Copy Architecture, the SDU Framework enables automakers to optimize data processing and storage while reducing environmental impact, supporting both business value creation and regulatory compliance.
On this page
Overview
The automotive industry leads the way in the data-driven revolution through connected vehicles, autonomous systems, and advanced customer insights. By 2030, global data production is expected to reach approximate 200 zettabytes , with automotive data being a major contributor. While data fuels innovation and growth, inefficiencies in data practices present significant challenges:
- Energy consumption: Data centers consume nearly 1% of global electricity (IEA).
- E-Waste: Rising infrastructure demands are projected to create 74 million metric tons of electronic waste by 2030 (UN E-Waste Monitor).
- Operational waste: Over 60% of enterprise data is unused, driving costs without adding value.
This whitepaper introduces the Sustainable Data Utility (SDU) Framework - a strategic approach to balancing data sustainability with business value creation. The SDU Framework leverages technologies like Zero Copy Architecture to promote:
- Purpose-driven data practices.
- Efficient processing and storage.
- Insights aligned with sustainability goals.
The SDU Framework empowers the automotive industry to maximize data potential while leading sustainable innovation.
Data Sustainability
1.1 The Challenge of Data Overload
The automotive sector is becoming increasingly data-centric, leveraging insights from connected and autonomous vehicles to drive innovation, but this growth introduces significant challenges:
- Connected vehicles: Each vehicle generates around 25 GB/hour of data through sensors, telematics, and infotainment systems. These data points include real-time diagnostics, driver behavior, GPS navigation, and environmental conditions. As more vehicles connect to cloud ecosystems, the cumulative data load grows exponentially.
- Autonomous vehicles: By 2030, each autonomous vehicle is expected to generate 4,000 GB/day due to the need for high-resolution imaging, LiDAR, radar, and AI-driven decision-making.
Without proper data management, this explosive growth leads to bottlenecks in infrastructure, inefficiencies in processing, and the need for constant hardware upgrades.
Underutilization of data:
- Despite the vast amounts of data being collected, less than 35% is actively analyzed or used The remaining 65% becomes “dark data,” sitting idle in storage systems. This results in:
- Wasted resources: Significant energy and computational power are consumed to store and maintain data that provides no business value.
- Missed opportunities: The inability to extract actionable insights from this data limits potential advancements in predictive maintenance, customer behavior analysis, and operational efficiencies.
1.2 Environmental and Business Impacts
The rapid growth of data-driven systems in the automotive industry has far-reaching environmental and economic consequences:
Energy Costs:
- Data centers, which are crucial for processing and storing automotive data, are one of the most energy-intensive components of digital infrastructure.
- Their energy consumption is projected to double by 2030, driven by the growing reliance on cloud services, AI processing, and the need for real-time data transmission in autonomous and connected vehicles.
- The carbon footprint associated with this energy usage poses a significant challenge for automakers striving to meet net-zero emissions goals.
Operational waste:
- Redundant and low-value data inflates costs across the board, from storage to network bandwidth.
- Unused data consumes valuable IT resources, leading to higher operational expenses without delivering meaningful outcomes.
- This inefficiency further impacts sustainability efforts, as more hardware and infrastructure are required to accommodate unused or redundant data.
E-Waste:
- Frequent hardware upgrades and the expanding infrastructure required to support increasing data volumes contribute to mounting electronic waste.
- Automakers risk falling out of compliance with environmental regulations as e-waste becomes a growing global concern.
1.3 Aligning data practices with industry goals
To address these challenges, the automotive industry must integrate sustainability into its data practices:
Net-zero emissions and circular manufacturing:
- Automakers are increasingly committing to net-zero carbon emissions and adopting circular economy models to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
- Achieving these goals requires rethinking data practices to ensure they support, rather than hinder, environmental objectives.
Optimizing digital operations for sustainability:
- Data sustainability must become a core enabler of the industry’s environmental strategies. This involves:
- Streamlining data collection to focus on high-value use cases.
- Reducing redundant processing and storage through intelligent filtering and smart compression techniques.
- Leveraging sustainable energy sources for powering data centers.
Regulatory alignment and competitive advantage:
- Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are placing increased emphasis on environmental accountability in digital operations.
- By adopting sustainable data practices, automakers will not only comply with regulations but also position themselves as industry leaders in green innovation, creating a competitive advantage.
SDU framework
2.1 A new paradigm for data management
The SDU Framework offers a purpose-driven approach to managing data, ensuring every stage of the data lifecycle maximizes utility while minimizing environmental and operational costs.
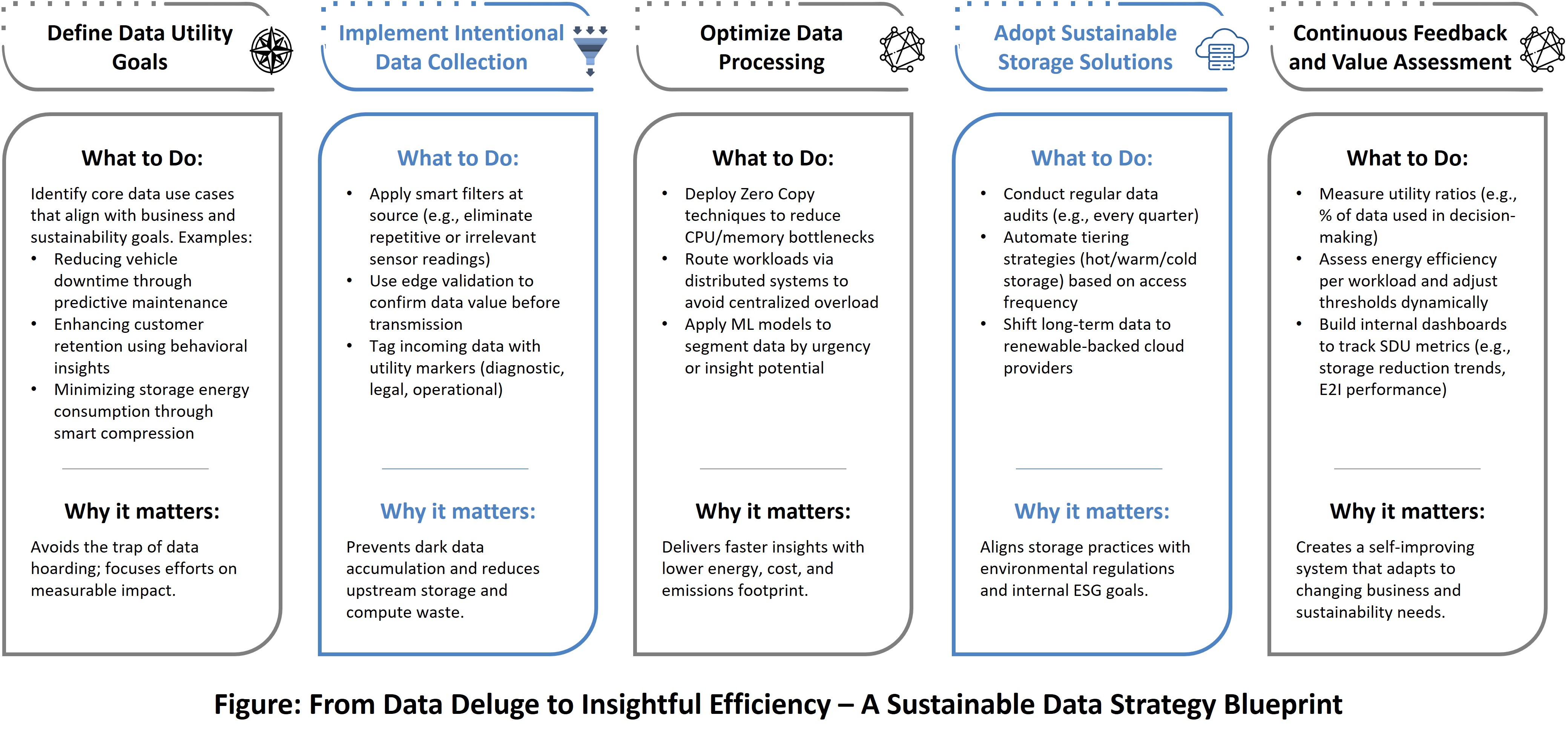
Purpose-Driven Data Collection
Focusing on collecting only the most relevant and valuable data ensures that resources are used efficiently, reducing unnecessary data overhead.
Aligning data with business goals
- Organizations should define clear objectives for data collection to avoid gathering unnecessary or redundant data. For example, collecting real-time diagnostic data for predictive maintenance rather than all telemetry data ensures relevance to business goals.
- Prioritizing specific use cases such as customer behavior analysis, predictive maintenance, or supply chain optimization ensures that data serves a purpose.
Smart filtering techniques
Technologies like edge computing and real-time validation can filter out low-value data before it is transmitted to the cloud or stored, reducing bandwidth and processing demands. For example, a connected vehicle may generate terabytes of raw sensor data, but only a subset (e.g., critical fault signals) needs to be sent for analysis.
Reducing unused data
Purpose-driven data collection minimizes the growth of “dark data,” ensuring that only actionable and valuable insights are extracted.
Optimized processing
Efficiently processing data can significantly reduce computational overhead, energy consumption, and environmental impact.
Energy-efficient architectures
- Using architectures like Zero Copy, which eliminates redundant data movement during processing, reduces CPU and memory usage. This directly lowers energy consumption while maintaining high performance. For example, predictive analytics models in autonomous vehicles can be optimized to process data locally instead of transmitting everything to cloud servers, reducing both latency and energy costs.
Leveraging AI/ML for efficiency
- AI and machine learning algorithms can be designed to prioritize energy-efficient computing while maintaining accuracy. For instance, AI models can identify patterns in data streams and process only critical data, ignoring irrelevant or repetitive inputs.
Distributed computing
- Shifting to distributed and edge-based processing systems reduces the load on centralized data centers. This ensures that data is processed closer to its source, cutting down on energy-intensive transmissions.
Sustainable storage
Efficient storage strategies ensure that only high-value data is retained, reducing costs and environmental impact.
Auditing and archiving
- Regular audits can identify and remove redundant or low-value data from storage systems. For instance, automakers can periodically review historical sensor data and archive or delete data that is no longer relevant to business use cases.
- Employing data compression technologies further reduces storage requirements without sacrificing data quality.
Tiered storage solutions
- Implementing tiered storage strategies ensures that critical data is stored in high-speed, accessible environments while less frequently accessed data is moved to cost-effective, long-term storage.
- For example, real-time diagnostics data can be stored on SSDs for immediate access, while historical data is archived in renewable-powered cloud systems.
Cloud-based sustainability
- Transitioning to renewable-powered cloud providers ensures that storage systems are environmentally sustainable. Providers like Google, AWS, and Microsoft Azure are increasingly offering carbon-neutral cloud solutions.
Actionable insights
Focusing on data that directly contributes to business outcomes ensures the data lifecycle adds measurable value to the organization.
Prioritizing high-impact use cases
- Aligning data collection, processing, and storage with business-critical use cases—such as predictive maintenance, vehicle optimization, and customer experience improvements—offers a high return on investment. For example, by analyzing sensor data from connected vehicles, automakers can provide personalized service recommendations, reducing downtime and improving customer satisfaction.
Real-time decision-making
- Actionable insights enable real-time decision-making, such as optimizing traffic flow based on connected vehicle data or adjusting supply chain operations based on predictive analytics.
- Integrating insights into decision-support systems ensures timely responses to business needs.
Automated feedback loops
- Continuously monitoring data utilization and impact through automated feedback loops allows organizations to refine processes and improve efficiency over time. For instance, analyzing the energy-to-value ratio of stored data ensures that low-impact datasets are removed or deprioritized.
By implementing these four principles, the SDU Framework ensures that data practices are purpose-driven, efficient, and aligned with sustainability and business objectives.
Enabling SDU
3.1 Zero Copy as a Supporting Technology
Zero Copy Architecture reduces energy and computational costs by enabling direct memory access, eliminating redundant data copying during transmission and processing.
3.2 Zero Copy’s Role in the SDU Framework
- Optimized processing: Reduces CPU cycles and energy use during data analysis.
- Sustainable storage: Prevents unnecessary duplication, lowering storage demands in applications like vehicle diagnostics and predictive maintenance.
Five-Step Framework
The Five-Step SDU Framework provides a structured approach to embedding sustainability across the entire data lifecycle. From defining data utility goals aligned with business and ESG priorities, to enabling continuous feedback loops that measure energy-to-insight efficiency, this framework ensures that every byte of data serves a purpose. By integrating smart collection, efficient processing, sustainable storage, and actionable impact tracking, organizations can transform their data operations from high-cost, high-waste systems into lean, future-ready engines of insight.
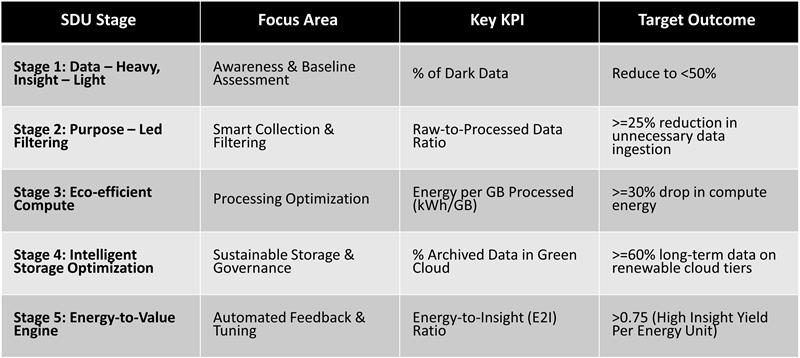
SDU Maturity Model: From Awareness to Optimization
This model provides a progression path for organizations implementing the SDU Framework - allowing them to benchmark their current state and define next steps across data sustainability.
Measuring Success
What gets measured gets optimized - and in the case of sustainable data, measurement is the bridge between ambition and action. To assess the effectiveness of SDU implementation, organizations must track performance not just in terms of volume or speed, but across utility, energy efficiency, and cost alignment
5.1 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Data utility score: Ratio of actionable or insight-generating data to total collected data. It encourages intentional collection and reduces dark data footprint.
- Energy efficiency ratio: Energy consumed per GB of processed data. It links computing performance directly to environmental impact.
- Operational cost savings: Reduction in infrastructure and storage-related costs due to optimization. This highlights the dual benefit of sustainability and business value.
5.2 Case study: SDU in Action
A global automotive OEM adopted the SDU Framework across its connected vehicle data operations. Before implementation, nearly 60% of data was unused, and annual energy costs exceeded $1M for storage and compute.
Before SDU: 60% of data was unused, and energy costs exceeded $1M/year.
After SDU implementation:
- 30% reduction in data movement and associated processing energy via Zero Copy
- 40% drop in storage costs through smart filtering and green-tier archiving
- 20% improvement in operational efficiency driven by predictive maintenance insights
These results demonstrate that SDU is not just a sustainability play - it’s a strategy that drives measurable business value, system performance, and future readiness.
Conclusion
The future of data in the automotive industry is not just about volume or velocity - it’s about responsibility, relevance, and results. The Sustainable Data Utility (SDU) Framework empowers automakers to reimagine data not as a burden, but as a lever for efficiency, innovation, and environmental stewardship.
By embedding sustainability principles across data collection, processing, storage, and insight generation, organizations can:
- Significantly reduce operational waste
- Meet growing regulatory and ESG mandates
- Derive higher value from smaller, smarter datasets
With technologies like Zero Copy, AI optimization engines, and renewable - powered infrastructure, SDU becomes more than a framework - it becomes an operating philosophy for the next era of digital automotive leadership.
Looking ahead, SDU also lays the foundation for AI-centric, quantum-ready, and circular data ecosystems - where every byte is measured by its purpose, and every insight is earned sustainably.
The time to act is now.
Automotive leaders who operationalize sustainable data today won’t just meet tomorrow’s expectations - they’ll define them.